TENS machine purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- The most important facts in brief
- TENS devices support muscle building and combat muscle as well as joint complaints.
- TENS therapy is used in the fields of medicine, rehabilitation, sports and wellness.
- Stimulation current devices stimulate nerves with the help of current, which is absorbed via electrode pads through the skin.
- A distinction is made between the TENS and EMS methods, which pursue different goals.
- Interested parties should study the subject in depth before making a purchase decision and, if necessary, seek medical advice – especially in pain therapy.
What is a stimulation current device?
TENS units are stimulation current devices that assist in both natural muscle building and nerve stimulation. The four letters TENS stand for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. Transcutaneous means that the electrical impulses are received through the skin. These electrical stimulation devices emit current pulses at a low frequency and are therefore harmless. Nevertheless, the devices should not be used by some groups of people or only with medical consultation. A distinction is made between the TENS and EMS methods. They pursue different goals. In general, the treatment with stimulation current devices is called stimulation current or electrotherapy. In terms of price, the products range from 20 to almost 200 euros.
The task of TENS devices
The goals and tasks of stimulation current devices are very diverse. This is because there are so many areas of application. First of all, interested parties should note the difference between TENS and EMS. There is a more detailed description about this in the section “Stimulation current models”. Nevertheless, the functional possibilities of these devices overlap in some respects. The points listed below apply generally to TENS, EMS or combination devices. These are the task areas at a glance:
- Muscle building
- Muscle strengthening
- Muscle relaxation
- Nerve stimulation
- Pain relief
- Pain therapy
- Physiotherapy
- Massage
- Wellness
For whom are TENS products interesting?
In principle, stimulation current devices can help all groups of people who suffer from pain in muscles, joints, bones or nerves. The origins are numerous. For example, someone who sits in front of a computer for several hours a day often has problems in the back and neck area. Competitive athletes who want to return to training as quickly as possible after an injury often have to contend with long rehabilitation phases. Even sportspeople who simply want to build muscles more quickly sometimes turn to stimulation current therapy to accelerate muscle growth or loosen muscles. Thus, these products are interesting for a large group.
Known brands
Prorelax | Beurer | Auvon | Sanitas | Saneo | Promed | Dittmann
For whom are TENS devices not suitable?
There are some groups of people who should only work with stimulation current devices in consultation with a doctor. These include pregnant women, people with pacemakers or implants or already known cardiac arrhythmias, minors, women with hormonal IUDs and people with Parkinson’s disease or epilepsy. Caution is also advised in the case of existing mental illnesses. Talk to your doctor rather once too much than once too little.
These are the advantages of TENS products
Because the tasks and the application possibilities of stimulation current devices are so varied, numerous advantages can be listed. Disadvantages are actually few. These are the most concise advantages and disadvantages:
Pro points
- Scientifically recognized
- Safe & low risk
- Direct mode of action
- Painless treatment
- Efficient & simple
- Suitable for on the go
- Inexpensive purchase
- No drug treatment
- Can be used individually – also prescribed by a doctor
- No device maintenance necessary
Drawbacks
- Application breaks must be observed
- Possible habituation effect with too intensive application
- Not suitable for some people
Since treatment with stimulation current devices is not a drug therapy, there are accordingly no interactions with other drugs. This is an important factor especially for patients with a history of health problems. For this group, electrotherapy for pain relief can, if necessary, reduce the use of painkillers or even replace them.
In addition, stimulation current therapies are recognized by health insurance companies. However, it is important to clarify possible cost coverage with the insurance company before starting a prescribed therapy. In most cases, patients can expect that no side effects will occur if the therapy is used correctly. However, if you experience increased pain or other discomfort, consult a physician.
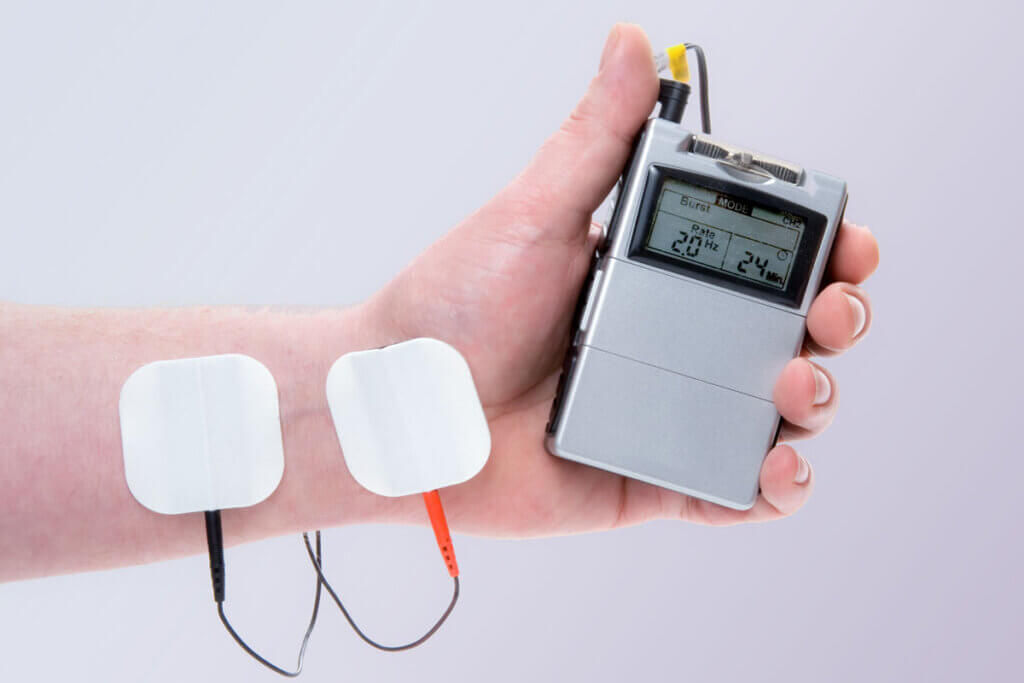

Wide range of applications
The two main areas of application are pain or nerve therapy and targeted muscle growth. In the first area, it is often the case that doctors prescribe therapy and, if necessary, accompany it medically. The second area of application often covers independent use – without medical accompaniment. However, there may be other situations where, for example, a physiotherapist constantly accompanies muscle growth after surgery.
Stimulation current devices are used for people who suffer acutely, but mostly already chronically, from physical complaints or tension. In the context of pain or physiotherapy, TENS products help to get the pain under control more quickly. They are used for rehabilitation and also complementary to massages. In some cases, they even replace high-priced massages. This may be of interest to people whose therapies are not covered by health insurance.
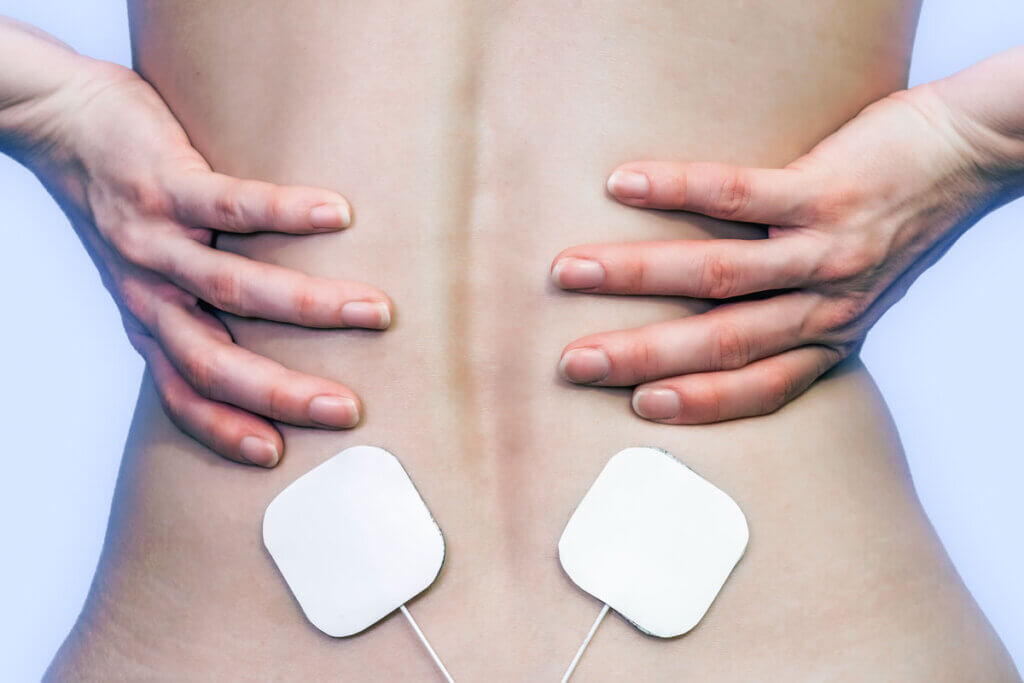
Relieve chronic ailments
TENS units are used to relieve chronic conditions throughout the human musculoskeletal system. These include, for example:
- Nerve pain
- Muscle pain
- Joint pain
- phantom pain
- Tension
- Pain after sports injuries
- Pain after surgery
- Tennis elbow pain
- Bone inflammations
- Rheumatism
- Herniated disc
- Lumbago
- Arthritis
Muscle stimulation
Furthermore, consumers also use stimulation current devices when they want to strengthen or build up their muscles. This can be helpful after an operation, for example. But athletes who want to build up their muscles specifically to achieve better performance can also use such a device.
Other applications
In fact, there are other areas of application where stimulation current devices help. They are also used for migraine, headaches, circulatory problems, incontinence or gastrointestinal problems. Some doctors also recommend their use as a complementary treatment after strokes or for paralysis symptoms.
Since stimulation current devices stimulate the metabolism, some users also use the devices simply to be able to relax better. Those who can relax more easily also release more of the body’s endorphins, or happy hormones. The very fact of relaxation can bring about relief from tension and pain.
Not to be understood as a substitute for sport
An electrostimulation device in no way replaces active sports or a healthy diet. It functions as a sports or therapeutic supplement. Physical endurance is not trained when using stimulation current.
How TENS units work
Electrical impulses, which reach the body through electrodes via the skin, i.e. transcutaneously, have a supporting effect on healing processes. This is the principle of stimulation current devices. They therefore function very similarly to a pacemaker. Trigger points are stimulated by electrostimulation. The electrodes are usually not integrated into the device, but are built into pads that are placed on the skin. Users apply these pads to the affected areas of the body – nerve pathways and muscle groups. This can be on the back, neck, abdomen, shoulders, arms or legs.
If you are unsure about the positioning, frequency settings and frequency of use, you can either consult your doctor or ask at pharmacies or medical supply stores. The instructions for use supplied also help with initial use. The products usually consist of the battery-powered device and two, four or more electrode pads.
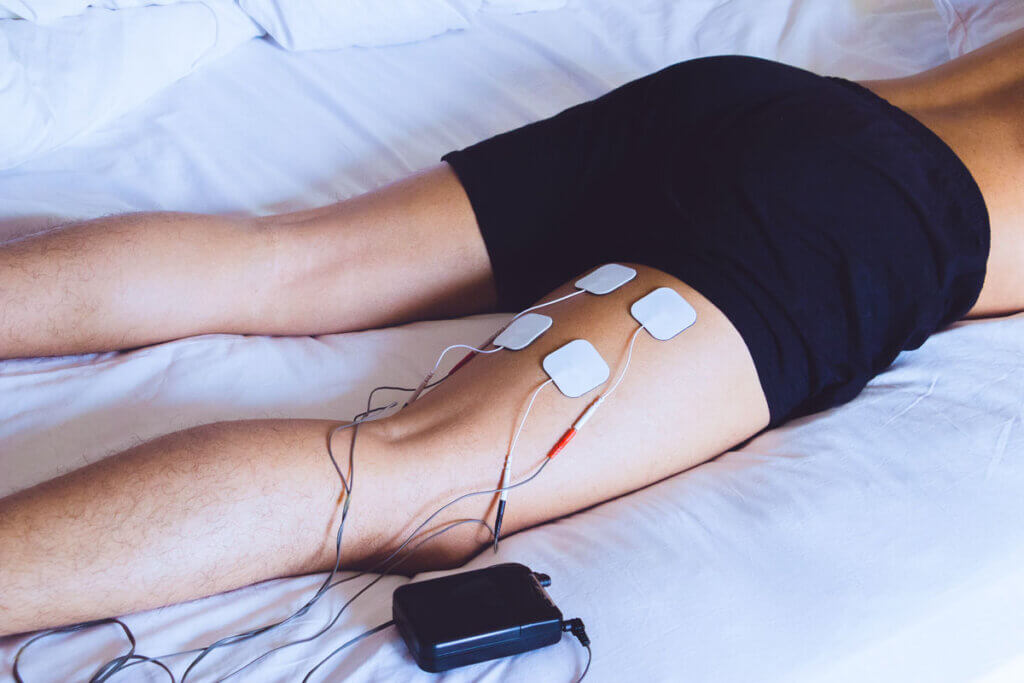
The Gate Control Theory
Because the current impulses delivered to nerve and muscle tissue are so gentle, users do not experience any unpleasant pain. This type of stimulation, often perceived as a tingling or vibrating sensation, elicits the body’s own responses that promote the healing process. The way TENS units work goes back to the gate control theory. It states that by stimulating receptors that transmit pain to the brain, the actual pain is masked. The body also releases endorphins and enkephalins, which are natural, endogenous opiates. They complement the so-called pain blockade.
The different stimulation current models
Applied stimulation current therapy has several advantages for pain sufferers. Interested parties should inform themselves in advance about the different applications of TENS and EMS. The two methods are often confused. The abbreviations reveal what which devices are to be used for. In short, the difference lies in the nerve or muscle stimulation. Both are done with the help of stimulation current, but with different strengths. However, the market also offers combination devices that combine TENS and EMS.
TENS method: pain therapy
The abbreviation TENS does not stand for “transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation” for nothing. This method is about providing patients with targeted pain relief. Because the areas of application are so numerous, these products are suitable for many people with pain problems. However, stimulation current devices can also be used alone in consultation with a doctor. To prevent muscle imbalances, it is recommended to seek professional advice. The frequency setting options are higher than with EMS devices. Some products offer the TENS method, but are additionally equipped with EMS as an extension.
Pro points
- Stimulates nerves
- Relieves chronic pain
- Promotes blood circulation
- Stimulates metabolism
- Releases endogenous substances
- Numerous areas of application
- Muscle relaxation as with EMS also possible
Drawbacks
- Often consultation with doctor necessary
- Attachment of the electrode pads without support sometimes difficult
- Not suitable for some people
- Muscular imbalances with overload
EMS Method: Fitness
Compared to TENS therapy, the EMS method is used specifically for muscle stimulation. This method is considered complementary to active sports as a kind of whole-body training and promotes muscle growth. Athletes also use the EMS method – electro-muscle stimulation – to warm up their muscles before training. The current frequency is set so low that users only feel a slight tingling sensation. The nerve pathways are not usually stimulated by this method. Blood flow is nevertheless stimulated, even at low frequencies.
What types of electrode pads are available?
The type and number of electrodes can be decisive purchasing criteria. With all types, it is important to make sure that the pads adhere firmly to the skin during treatment. If this is not the case, the transmission of the stimulation current through the skin will not work properly. There are self-adhesive pads, permanent electrodes or textile electrodes. Depending on the device, the pads are connected to the operating device by cables. Users apply them directly to the painful area or near the desired part of the body. The devices usually have two, four, six or eight pads. Buyers pay attention to material composition, workmanship, number and size.
Self-adhesive pads
Most devices have self-adhesive electrode pads that function like a Band-Aid. For these, users do not need a supplementary contact gel because they stick on their own due to their surface texture. They usually consist of three layers: textile insulation layer, metal strips with current, adhesive layer with conductive gel.
Pro points
- Adhere independently
- No gel necessary
- Easy application
- Hygiene aspect
Drawbacks
- Adhesive strength decreases
- Pad replacement necessary after some time
- Follow-up costs
Permanent electrodes
This type of electrode is made of silicone or natural rubber mixed with a conductive material and is therefore more stable than the self-adhesive variant. Insofar as the conductivity of permanent electrodes is very strong, users have to make compromises in terms of flexibility. In addition, the use of a contact gel is necessary. This can be more cumbersome, but offers the advantage that cleaning is easier.
Pro points
- Very long durability
- Easy cleaning
- Good hygiene
Drawbacks
- No self-adhesion
- Contact gel necessary
Textile electrodes
The market also offers textiles consisting of conductive material. These can be, for example, cuffs for joints, socks or gloves. The electrodes are integrated into the material in the form of metal threads. Silver is often used.
Pro points
- Uniform stimulation
- Applicable over a large area
Drawbacks
- Less selective application
- Hygiene aspect
Other types of electrodes
Manufacturers also offer probes, clamps or suction cups for other applications. The so-called abdominal belt belongs to the textile electrodes and is more in the area of the EMS method.
These purchase criteria help with the decision
As already mentioned, the type of electrodes is one of the most important aspects of TENS units. But also the number of pads and the channels to be controlled are decisive for a purchase decision. Here, interested parties should consider in advance whether they want to perform a punctual or a symmetrical, large-area therapy. Furthermore, it is advisable to research the respective program functions of the stimulation current devices before buying.
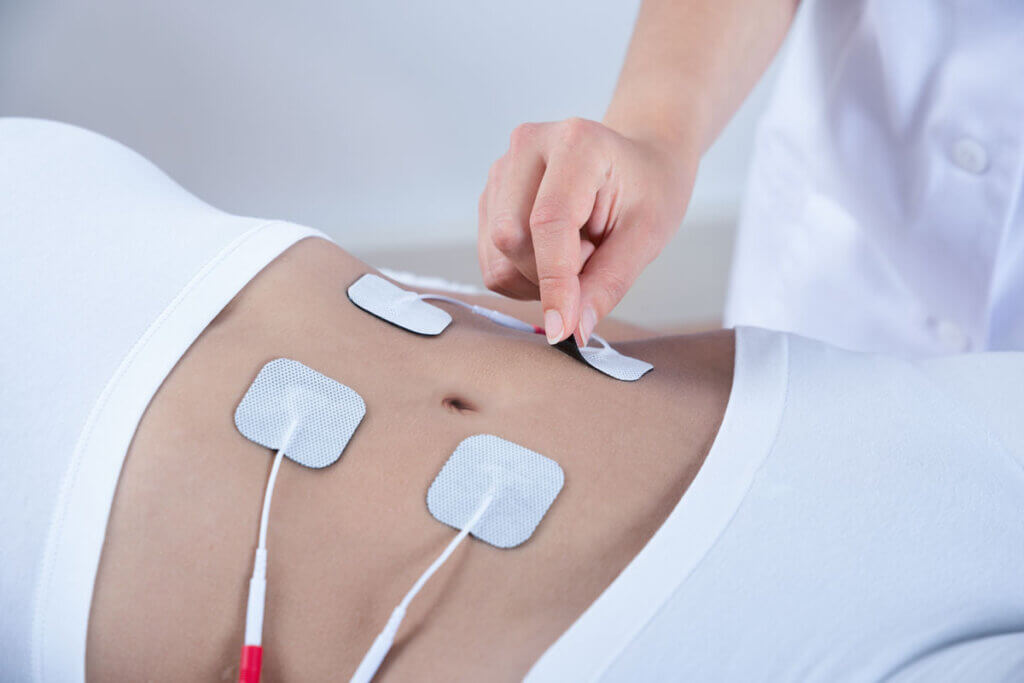
The more individual the needs, the more program options should be available. It is worth comparing, as many devices are not necessarily much more expensive, even if they offer numerous options.
In addition, consumers best still pay attention to the possible frequency ranges, intensity levels as well as current strengths. The function of an automatic shut-off can also be helpful to avoid overuse. Keep in mind that you should seek professional advice before using it for the first time. You can learn more about the individual criteria below:
What are the number of channels and pads?
For example, there are 1-channel, 2-channel or 4-channel stimulation current devices, each of which has two, four or eight electrodes. Two electrodes are assigned to each channel. So there are always pairs. It makes sense to control the channels separately, many devices can do this. As a rule, users with a small number of electrodes are more likely to perform selective treatment. If you want therapy over a large area, you should look for devices with several channels and correspondingly more electrode pads. If necessary, discuss this with a doctor or ask at a medical supply store.
Number of programs: TENS vs. EMS
Combination devices with a variety of programs make sense for users who do not want to choose between the TENS and the EMS method. Here, individual programs can often be set and even saved. In this way, users tune the programs to their own needs and, if necessary, adjust the settings again and again during therapy. For example, there are also TENS models with an integrated massage function.
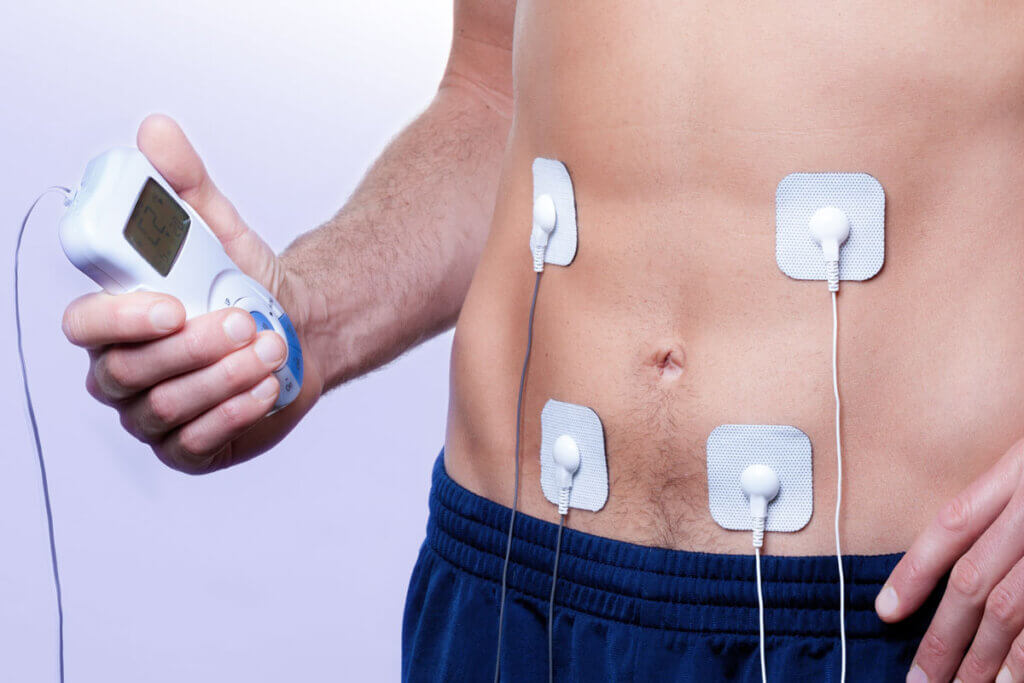
Massage programs
Many models offer different massage programs. If you focus on relaxation, it’s best to choose a device with up to ten massage functions. Often, these devices are not much more expensive than those with fewer massage options. A comparison is worthwhile.
Automatic switch-off
The automatic switch-off of a stimulation current device is useful to protect against overload. If you do too many spot treatments too often, you can trigger muscular imbalances. This must be avoided at all costs. An automatic switch-off function ends the therapy without the user having to intervene manually.
Output frequency
The frequency describes how many pulses run through the stimulation current device within one second. The unit is always given in Hertz (Hz). TENS units work with frequencies of at least 2 Hertz up to 150 Hertz.
Frequency ranges
One can divide the treatment with stimulation current into four ranges, each with different goals. At this point, the EMS treatment is not mentioned, it is information about the TENS therapy. We show the effect of the different intensities in the following:
| Frequency range | Effect | Treatment goal |
| Less than 10 hertz | single twitches, vascular muscles are stimulated | Muscle relaxation |
| Between 10 and 20 hertz | Fibrillations (spontaneous twitches), intestinal muscles are stimulated | Strengthen pelvic floor muscles |
| Between 20 and 80 Hertz | Tetanic contraction, increased stimulation of muscles | Joint pain treatment |
| Above 90 Hertz | Increased contraction of muscles | SchmerzbehaPain treatmentndlung |
Patients who receive therapy with a Hertz frequency between 80 and 150 usually perceive pain relief. They feel a kind of tingling in the otherwise painful part of the body. In the lower frequency ranges, the pain is said to be dulled. The longer the pain has been present before, the more therapy sessions are usually needed to achieve long-term improvements.
Do not ignore additional pain
If additional pain develops, patients should immediately discontinue therapy and seek medical advice before continuing with planned use.
Which intensity level makes sense?
The intensity level must be matched to the pulse frequencies. These two criteria are interdependent. Again, anyone who is unsure should ask a doctor for advice, even if self-therapy is the goal. Users apply low frequencies together with higher intensity in stimulation current therapy – and vice versa.
Maximum current intensity
The maximum current intensity is measured in the unit milliampere (mA). It denotes the strength of the flowing current, i.e. the highest possible intensity level. As a rule, a TENS unit has a maximum current strength of 50 to 80 milliamperes. Beginners use lower amperages than experienced consumers.
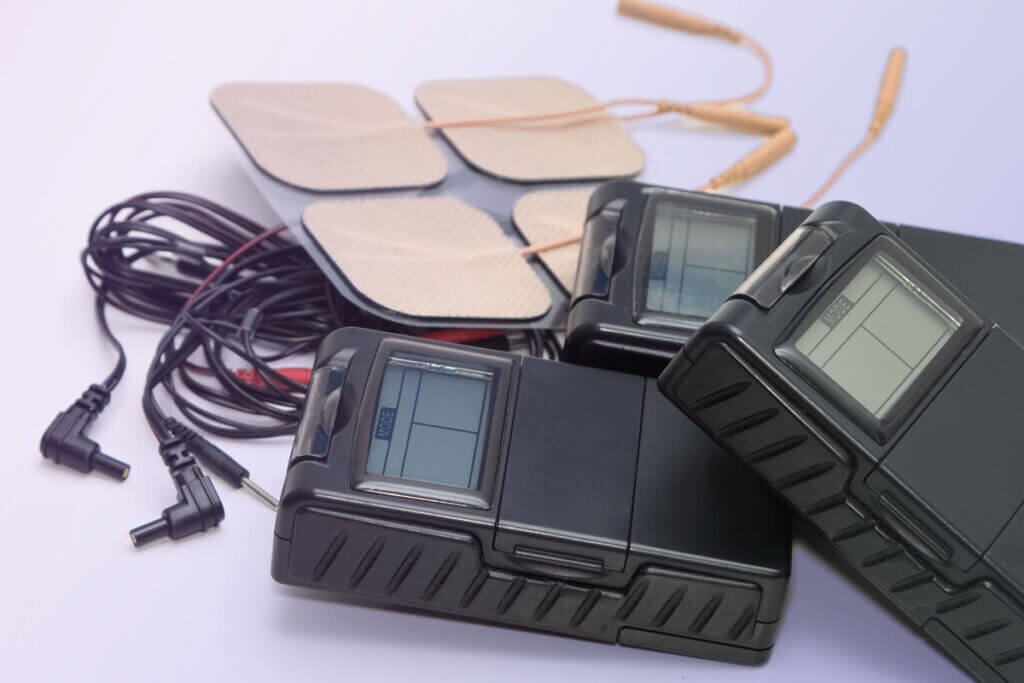

It makes sense if devices offer the option of setting the current strength individually. This allows users to try out which strength suits them best on which days. After all, the body’s sensitivity varies from day to day or from week to week.
Pulse duration
Pulse duration, also called pulse width, is measured in microseconds (μs). Thus, the unit denotes the duration or width of the pulses per second. Normally, a TENS value is between approximately 80 and 200 microseconds. The higher the pulse duration, the deeper the current pulse goes.
Pulse shape
With the pulse form one speaks also of the flow direction of the current. The current can flow either in one direction, monophasic, or in both directions, biphasic. If the pulses flow in both directions, the muscle is relieved more than with the monophasic pulse form. Accordingly, devices with a biphasic pulse shape are more recommended if users also set only low frequencies.
Power supply
Manufacturers offer TENS units with rechargeable batteries, batteries or power supplies. The most common form is the one with batteries. It is recommended to choose a product that displays the battery charge level so that the therapy is not interrupted unintentionally. Rechargeable batteries and batteries offer maximum flexibility. Users can take the devices with them to any place. A few products have a power supply unit.
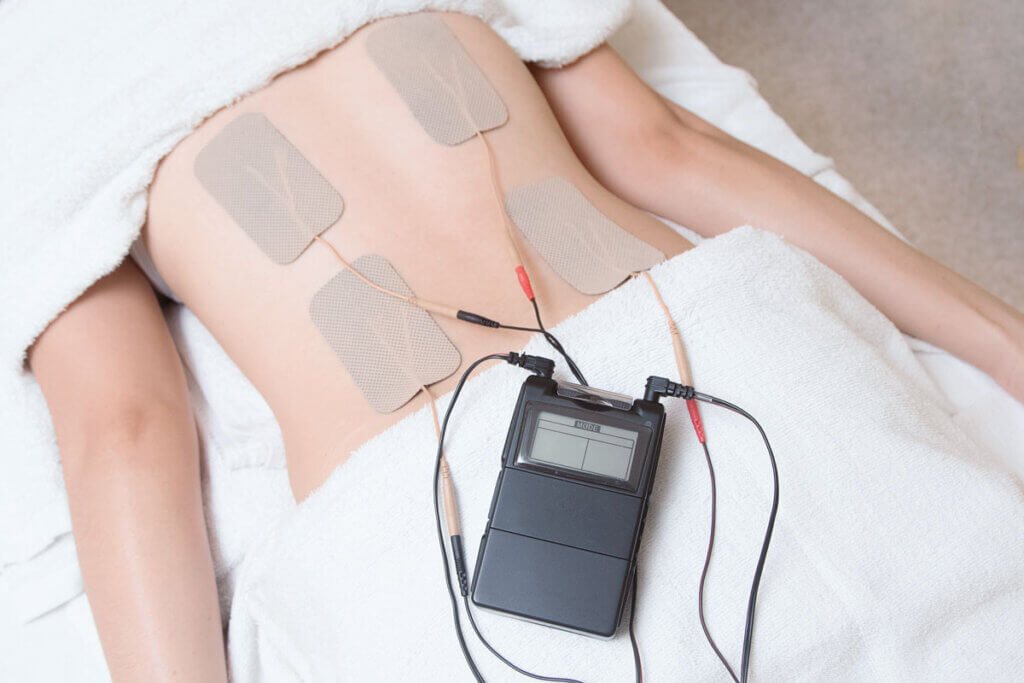
Although there are no follow-up costs for buying more batteries, the advantage of flexible use is lost. The durability of the batteries used depends on the frequency of use. As a rule, good quality batteries last just under three months with daily use or use over several weeks.
Other functions
Most TENS products have an LC display, via which the operation takes place. It should be easy to read and at best have a backlight. Especially consumers who use a TENS unit for the first time need an intuitive handling and a good user manual.
TENS products are usually no larger than a smartphone and weigh no more than 150 grams. Also of interest is the option of a universal connector for the electrodes. Some manufacturers also include replacement electrodes or other pad sizes.
For storage, the purchase of a belt pouch makes sense, if it is not included. The market also offers specially designed pouches. Since these are products for medical use, storage is an important aspect for reasons of hygiene.
























 17,139 reviews
17,139 reviews


