Spin bike purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- What You Need to Know
- Indoor cycling is good for the cardiovascular system. Athletes improve their endurance and train their muscles.
- Whether you are a hobby or professional athlete, the training can be adapted to any level.
- Sports enthusiasts should pay attention to the differences between exercise bikes and indoor bikes when buying.
- Exercise bikes are well suited for beginners who want to do an easy to moderately difficult workout.
- Professionals are better off using speed bikes for very demanding training sessions.
- a comparison of the best indoor bikes
What is an indoor bike?
Indoor bikes, also called indoor cycles, simulate cycling on the road within your own four walls. Originally, professionals from the cycling scene developed this fitness equipment in the 1970s in order to be able to prepare optimally – regardless of weather conditions and temperature – for their competitions. The goal was and still is to make the training as realistic as possible.
Today’s indoor bikes, however, not only serve the training needs of cycling professionals, but are also suitable for amateur athletes and absolute beginners. Although in many ways they are comparable to a real outdoor bike, there are some concise differences. Before buying an indoor bike, interested parties should inform themselves about the terminology, because the market offers indoor bikes or indoor cycles, spinning bikes, speed bikes and exercise bikes.

Spinning bike
The word “spinning” has been copyrighted by the manufacturers Star Trac and Spinning. Other brands are not allowed to use the word combination spinning bike, which is why they fall back on “spinning bike”, “indoor bike” or “speed bike”, for example. As a rule, however, the features and uses of these products are similar.
Good to know
Although the terms are often used synonymously and the products are also very similar, not every indoor bike is automatically a spinning bike.
Indoor cycle and indoor bike
Indoor cycles and bikes are indoor bicycles for use at home. Their design is usually simple and sporty. Training sessions with these machines help riders gain more strength and endurance. Unlike exercise bikes, indoor bikes usually do not have a freewheel. The flywheel and crank arms are coupled. If the rider stops the workout, the flywheel continues to turn – or the rider applies the brake manually.
Speed bike
As the name implies, the use of speed bikes is usually designed to allow sports-motivated people to train intensively on the machine. Professional cyclists who want to specifically improve their endurance train on speed bikes. Here, for example, the handlebars are aligned similarly to a real racing bike, so that the rider leans very far forward on his arms during the training session or even rides standing up. Riding while standing is what professionals call the cradle pedal.
The advantages of indoor bikes
Regular workouts benefit the cardiovascular system. The focus is on improving strength and endurance in the long term. This applies to beginners as well as professionals, because indoor bikes are suitable for anyone who would like to exercise more often at home. Compared to jogging, training on bikes has the great advantage that it is easy on the joints. For example, in addition to indoor bikes, there are also exercise bikes that people with health problems can use to exercise while lying down. However, you should seek medical advice before using them if you have health problems.
Depending on the desired intensity of the training and the choice of product, riders can, for example, simulate the ascent of a mountain by adjusting the pedalling resistance on the device. Enthusiastic road cyclists not only simulate the mountain, they also get the feeling of a real road bike ride. In a normal upright position, they mainly train the gluteal and thigh muscles. All types of indoor bikes are also suitable for losing weight and reducing fat.

What distinguishes indoor bikes from exercise bikes?
Exercise bikes are not to be confused with indoor bikes or cycles. Even if the training goal of improving one’s fitness overlaps, the differences can be decisive when choosing. Indoor bikes are more geared towards an athletic sitting or standing position compared to exercise bikes. Therefore, they are very suitable for performance-oriented workouts. Exercise bikes, on the other hand, are more versatile and promise gentle and back-friendly workouts. This means that calorie consumption can also vary. Indoor or spinning bikes and exercise bikes also differ in terms of flywheel size, freewheel and different braking and display systems. Another important difference is the power rating: exercise bikes indicate the braking resistance in watts, i.e. electronically, while speed bikes indicate it in steps, i.e. mechanically.
Indoor bikes for performance-oriented athletes
Indoor cycles are characterised by performance-oriented training possibilities. This is mainly related to their large flywheel. Riders can use very high pedalling frequencies and resistances, and the wheel is always coupled to the crank arms. There is no freewheel: as soon as the disc is in motion, the arms automatically rotate with it, resulting in a smooth ride. In addition, the direct power transmission helps to train effectively. The brake works mechanically; therefore, it is not possible to measure the power in watts.
Training on indoor bikes is very quiet. The machines promote an athletic riding position that is very similar to that of a racing bike – both sitting and standing. Indoor cycles or speed bikes tend to be suitable for losing weight quickly. However, their use is more recommended for people without health restrictions.
Exercise bikes for training that is easy on the joints
Exercise bikes score points with their gentle training options. The machines also work well for cardio training for people who value a comfortable sitting or lying position. Compared to indoor bikes, exercise bikes have a much smaller flywheel and an installed freewheel. The brake is electronic. With high-priced machines, exercisers can set the wattage themselves. They are therefore versatile and recommended for people who cannot sit in a racing bike position due to back or joint problems.
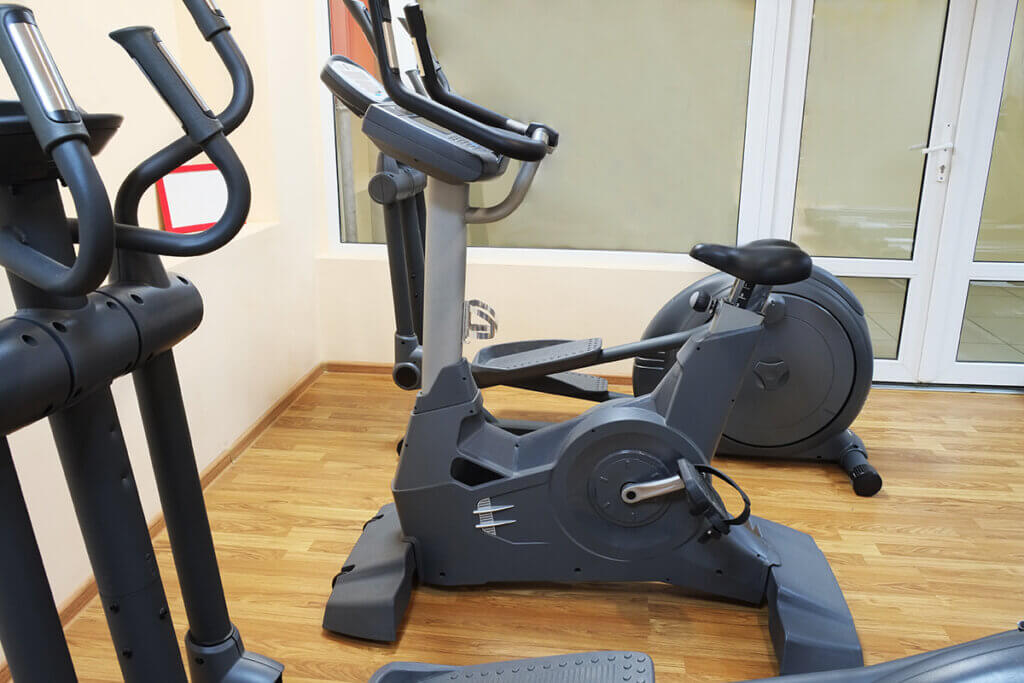

Some exercise bikes offer multimedia displays and pre-installed training programmes. However, unlike indoor bikes, some exercise bikes in the budget price categories do not have a perfectly round step, which professionals might find annoying.
What to look for when buying indoor bikes?
Before buying, sports enthusiasts should be clear about the types of training they want to do in the future. In addition, health aspects can be decisive in determining which product is best for you. Different saddle, handlebar and pedal settings are among the most important purchase criteria. Stability, the braking system, the flywheel mass as well as the operation and, of course, safety are also decisive. Overall, the material and workmanship should be of high quality.
Well-known brands
LeMond | Life Fitness | Miweba | Taurus | Kettler | Peloton | Asviiva | Sportstech
Saddle and handlebars
An ideal, ergonomic seating position is essential. Most indoor bikes have seats that are very similar to road bike saddles. These should be adjustable to your own body size. The material should not chafe. Leather saddles are only offered by the high-priced products. Some professional cyclists may want to fit their own saddle to their speed bike. The handlebar material should be grippy and non-slip; foam is recommended. Here, too, the handlebar position should be adjusted to the body size.
Pedals
As on a real bicycle, a stable grip on the pedals is important on an indoor bike. Cyclists should feel safe at all times. For more grip, there are adjustable straps or special click systems, but you usually have to buy them separately. These guarantee a firm connection between shoe and pedals.
Load capacity and weight
The maximum load capacity of most speed cycles is between 120 and 150 kilograms. The exercise bike itself should be as stable as possible and should not move during training. Many indoor and spinning bikes weigh between 20 and 40 kilograms. Caution: Some bikes can only be used up to a body weight of 100 kilograms. Find out in advance about the possible use.
Braking system and resistance
You can choose between a magnetic and felt shoe brake. Magnetic brakes are more expensive, but they work more quietly and have less wear. They have a contactless effect on the flywheel through a permanent magnet. Many speed bikes have a felt brake that can be adjusted. This presses on the flywheel of the bike and generates resistance; therefore it is also called a sliding brake.
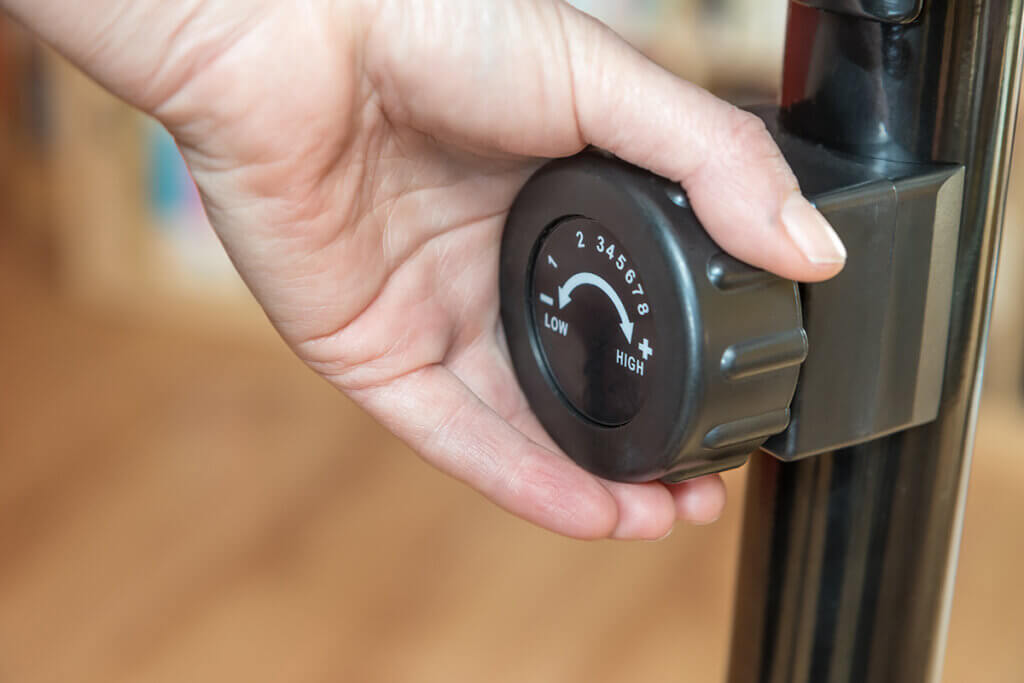

Manual brake
Indoor and spinning bikes that have a manual brake do not have pre-installed programmes. This is only possible on models, or more precisely exercise bikes, with electronic braking devices. However, some manufacturers offer mixed models that combine the advantages of exercise bikes and indoor bikes, so to speak. Indoor cycles without freewheel should always have an emergency braking device in case the rider slips off the pedals, for example. When choosing a bike, athletes should make sure that the emergency brake on the bike is easy to reach.
Drive
Chain-driven models give the rider a real outdoor riding experience. Although chain drives hardly make any noise, they are louder than models that have a belt drive. The belts are made of Kevlar or another plastic material and are undemanding in terms of maintenance. Chains, on the other hand, require maintenance every now and then – including greasing and oiling. Belt drives are therefore of higher quality, but also cost more.
Flywheel mass
One of the most important purchase criteria is the flywheel mass. In order to be able to exercise with a smooth pedal, the flywheel should weigh at least 16 to 18 kilograms. The larger the flywheel mass, the smoother the rotation. This also protects your joints when you ride at high pedalling frequencies.
Operation
For some sports-motivated people, pre-installed training computers that they set themselves on a display can be useful. This is where high-quality indoor and spinning bikes store personal training information. This can include a heart rate monitor, for example, which is either located on the handlebars or uses sensors on a chest strap to record the pulse information. In classic training sessions, however, riders tend to concentrate only on the cycling itself, preferably without distractions. Despite this, pulse-controlled training can be helpful in order not to completely exhaust one’s own limits of exertion. Training apps help with this.

What can training computers do?
Some bike models have a display on which riders can read the distance covered, speed and cadence, as well as the calories burned and time and pulse information. For devices that do not have a training computer, there is often the option of a subsequent installation. It is best to find out about the options beforehand. Using a training computer, professionals can sometimes even create their own training profiles to simulate mountain rides. Others offer fitness units that focus specifically on fitness or muscle building. A heart rate monitor is recommended for all exercisers.
Stability
Stability is one of the most important factors. Speed bikes with large, heavy flywheels, i.e. a high dead weight, guarantee stability. Not only should the seat and the rider’s position on the machine be stable, but the bike itself must remain in place during training – even at high pedalling frequencies and sprints. The entire frame of the model should therefore be robustly built.
Dimensions
If you want to train at home, you should be aware before buying that spinning bikes, exercise bikes and speed bikes take up a certain amount of space. The dimensions are similar to those of a normal bicycle. However, it is better to plan a little more space in the room than too little. Here are some examples of the dimensions – length times width times height:
- 104 x 54 x 116 centimetres
- 110 x 45 x 115 centimetres
- 130 x 55 x 124 centimetres
These additional features are interesting
A perfect bike has its price. This also applies to indoor bikes, where numerous features make the riding experience even better. These include pulse sensors on the handlebars or chest strap. A Bluetooth interface can be helpful to avoid the use of annoying cables if you also want to connect the spinning bike to other technical devices. The smartphone, for example, can display your own training data via Bluetooth, although it is then not possible to control it directly on the phone. Some models have an app for training planning and recording.

Extras for more comfort
For road cyclists who regularly do indoor cycling, there are some features that create a lot of comfort for a small extra charge. A water bottle holder allows ambitious riders to train for long periods without interruption. But hydration holders are also useful for training beginners if they get sweaty quickly. Manufacturers also offer an additional sweat guard, also called a sweat catcher, for indoor bikes. This is stretched between the handlebar and the saddle and protects the frame of the spinning bike.
Training with a tablet also requires a specific mount, otherwise riders have to constantly interrupt to make changes. Tablet holders make long training sessions more enjoyable.
There is also a comfortable feature for the handlebar device that protects the forearms from pain: padded arm rests. If you have already installed such supports on your outdoor racing bike, you should not do without them on your indoor cycle.
Features for placing a spinning bike
The weight of the bikes should not be underestimated. The heavy equipment cannot easily be pushed from one place to another. Transport wheels help with this. Some models even have these integrated. Another interesting feature is a height adjustment for the floor, in case the ground at home is uneven. Many spinning bikes have feet that can be adjusted manually. In addition, it can be useful to place a mat under the machine if the floor is sensitive.
Tips for training
The right spinning bike is ready and waiting in your own home. Now it’s a matter of motivating yourself again and again to develop and maintain your fitness. The following tips will help:
- Set a long-term training goal
- Proper preparation: sportswear, water, light food
- Create a training plan according to your fitness level: Endurance training, interval training, cardio training.
- Train regularly: two to four times a week at the most
- Listen to the body’s signals
- Take at least one day off between workouts
- Keep at it and have fun
How do I adjust my bike correctly?
The saddle and handlebars must be optimally adjusted to your own body size before first use. Every athlete should feel safe and comfortable. Most indoor or spinning bikes allow you to adjust the saddle up or down and also horizontally. Depending on your height and stride length – measured from leg and torso length – adjust the saddle so that you can easily reach the pedals and have a comfortable seat. The handlebars should be adjusted so that they are not too far away or too close to the upper body. Caution: Professional road cyclists adopt a very athletic position in which the arms bear a relatively large amount of weight. Beginners usually sit in a more upright position so that the arms experience little or no strain.
I train best in this heart rate range
Riders who train according to pulse are guided by the following formula:
- For men: pulse (maximum) = 220 – age
- For women: Pulse (maximum) = 226 – Age
The numbers 220 and 226 stand for heartbeats per minute (heart rate). This is the maximum pulse for healthy people, which they should not exceed when exercising. As a rule, the heart rate of older people should not be as high as that of young people when exercising. Of course, this also depends on the person’s fitness level.
The optimal heart rate zone can be determined with this formula once the exerciser has decided in which zone he or she would like to train. The zones are divided into health zone, fat burning zone, aerobic zone, anaerobic zone and warning zone (degree of exertion increasing).
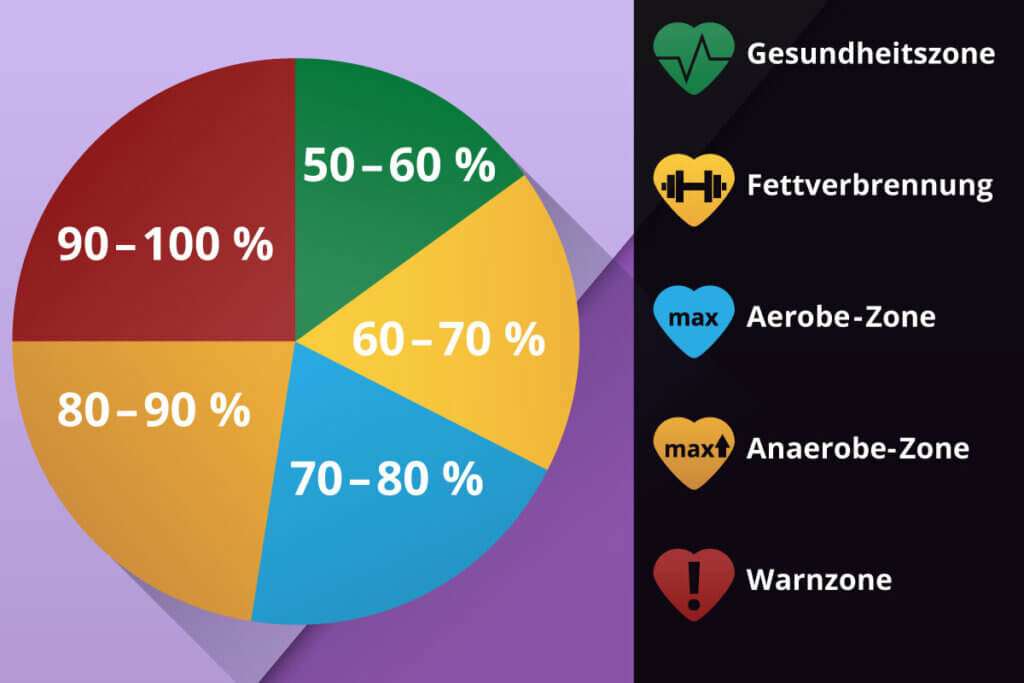
Let’s assume an athlete wants to train between the health zone and the aerobic zone, at about 50 to 80 percent of the maximum heart rate. Then the pulse zone is calculated as follows:
- Lower limit of the pulse zone = pulse (maximum) x 0.5
- Upper limit of the pulse zone = pulse (maximum) x 0.8
Athletes are in the healthy zone at these values. The load ranges from light to medium. Exercising in the warning zone at more than 200 heartbeats per minute is not recommended. Even competitive athletes should only do such training under professional supervision.
Common training mistakes
Less trained cyclists must be careful not to overdo the training sessions at the beginning. Do not go straight to your performance limit, but increase step by step. Athletes can achieve quick results in endurance and muscle building even with easy to moderately difficult units. Always take into account your own physical condition. Take the training slowly if you suffer from joint problems or back pain, for example. If riders feel more pain after training on the spinning bike than before, it is best to seek medical advice.
Also, motivated beginners sometimes make the mistake of not taking breaks between workouts. It is advisable to take at least one day off between sessions. The body needs this time to regenerate. If the breaks are not taken, the body will become exhausted after some time – the positive training effects will not be felt.
What is the most effective training?
Cyclists train best in a time frame of 45 minutes. In a 45-minute unit, body fat is reduced on the one hand and endurance is improved in the long term on the other. Of course, the training also strengthens the muscles. This training is suitable for all cyclists who already have some endurance but do not want to completely exhaust themselves. However, the degree of exertion also depends on the selected cadence. Absolute beginners can start slowly, increase slightly and cycle comfortably again for the last ten minutes. Professionals can integrate demanding intervals into their training. Interval training helps to improve endurance and speed in the long term.
Short and intense: cardio training
Shorter training units also have a positive stress effect. During cardio training, riders pedal with as much resistance as possible for a relatively short period of about 20 to 30 minutes. Additionally integrated training peaks serve to maximise the strain on the muscles – as is the case, for example, with the sway pedal. The motto for cardio: you train for a short time, but get maximum effect.



















 522 reviews
522 reviews



