Patio heater purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- The most important facts in brief
- Radiant heaters provide heat where conventional heating cannot be installed.
- Gas-powered radiant heaters are well suited for use on outdoor surfaces.
- Unlike gas heaters, electricity-powered radiant heaters can also be used indoors.
- In terms of energy efficiency, both variants perform poorly.
The flexible heat source
Radiant heaters are gas- or electricity-powered devices that supply their surroundings with heat. They are used where conventional heating cannot be installed. Most people know radiant heaters from outdoor catering areas. Because of their shape, the devices are often called mushroom heaters. However, radiant heaters can also be used in many different ways in the private sphere. They provide cosy warmth on the terrace, in the summerhouse or in the hobby cellar. Mobile radiant heaters can be set up flexibly wherever heat is needed.
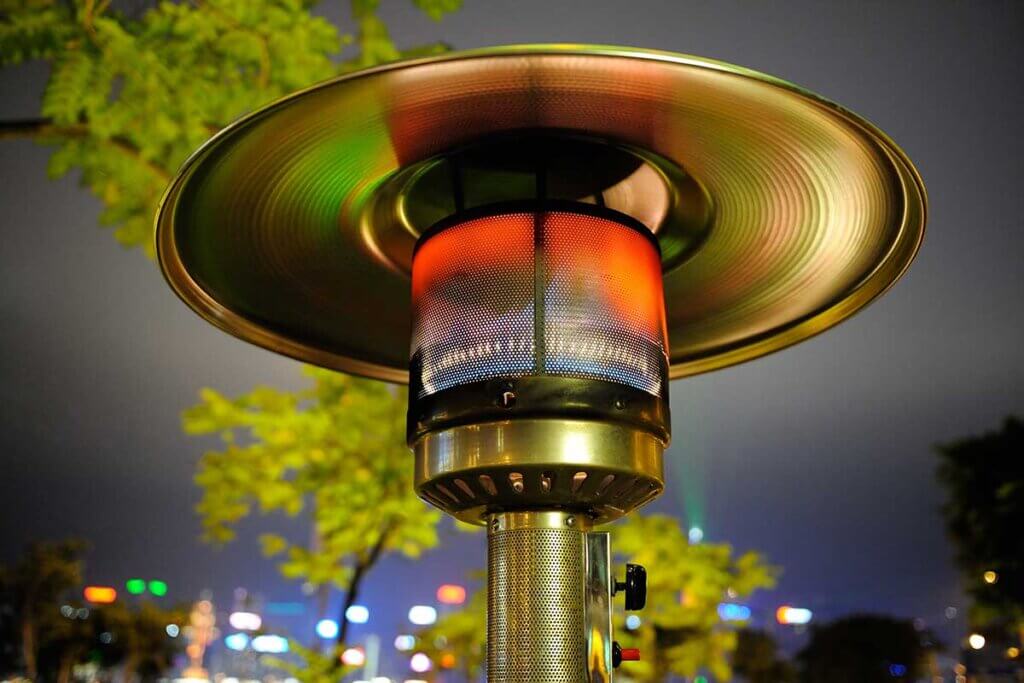

Radiant heaters may be practical, but they are also real energy sinners. Heating outdoor areas in particular wastes a lot of energy. That is why their use in the catering industry is banned in many cities – in Berlin, for example, since 2009. Their use in private areas, on the other hand, remains permitted. However, regularly switching on a radiant heater in the garden is anything but energy-efficient, because it only generates sufficient heat when it is at full power. Gas-powered devices emit carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides during operation and are therefore completely unsuitable for indoor use. Electric radiant heaters do not produce any direct emissions, but depending on the energy mix they have a similarly poor CO2 balance. Interested parties should thoroughly weigh up whether the purchase of a radiant heater is necessary. Outdoor operation in particular is not only detrimental to the climate, but also to one’s own wallet. Indoors, use only makes sense under certain circumstances.
Operating mode – gas or electricity?
Radiant heaters are operated with gas or electricity. The devices therefore differ in the way they heat their surroundings. Gas radiant heaters emit heat into the air. Electric radiant heaters, on the other hand, produce infrared radiation, which heats surfaces but not the air.
Gas radiant heaters – for large outdoor areas
Gas radiant heaters are the mobile solution for outdoor areas. They are prohibited indoors for fire safety reasons. They are operated with propane gas, usually 11-kilogram gas cylinders are used. When the flame of gas radiant heaters is ignited, it heats a radiating element and thus generates radiant heat. In front of the flame is a grille or glass that protects users from direct contact. Gas radiant heaters are made of stainless steel or other heat-resistant materials.
Gas radiant heaters are particularly impressive because of their high output, which allows them to heat even large areas such as terraces. Apart from this, however, they have some disadvantages compared to electrically powered devices. For example, the output can be affected by the wind. Then there are the running costs: new gas cylinders have to be purchased regularly for operation. Electric radiant heaters are much cheaper in this respect, although less powerful. Stand-alone units carry the risk of falling over or someone falling into them. Moreover, the flame in gas radiant heaters always poses a certain fire risk.
Pro points
- High performance
- Ideal for large areas
- Independent of cables
Drawbacks
- Can only be used outdoors
- Susceptible to wind
Electric radiant heaters – suitable for indoor use
Electric radiant heaters are powered by electricity and only require a socket in their vicinity. After connection, they are immediately ready for use. There is no need to handle heavy gas cylinders. The heating panel of electrically operated radiant heaters contains rods that are heated by a metallic heating coil, which produces heat radiation.
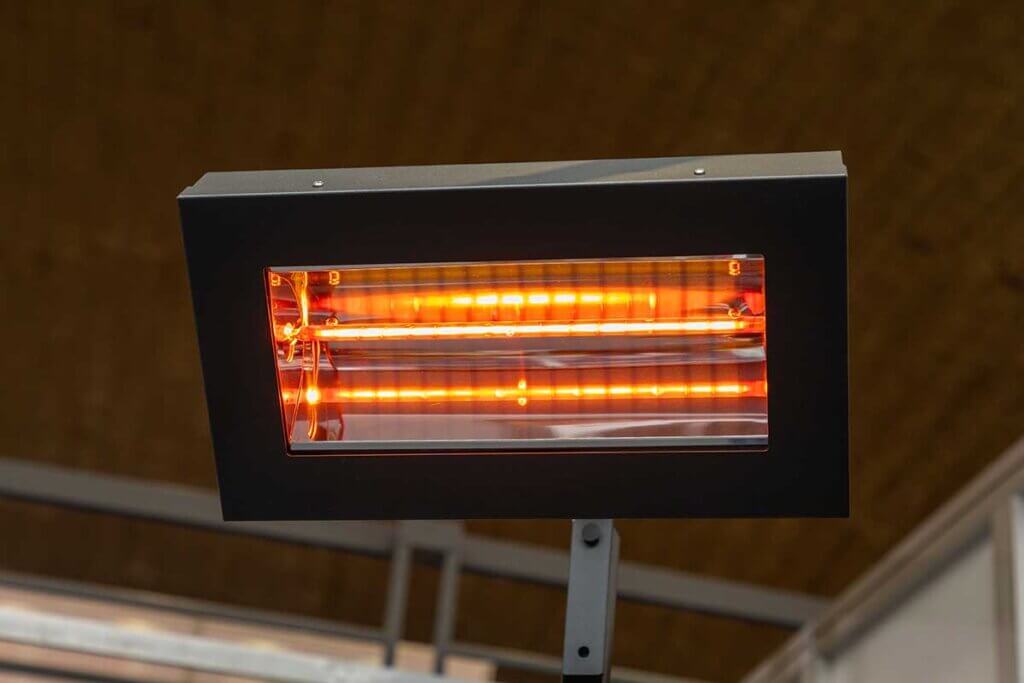

These radiant heaters are particularly suitable for indoor spaces where the use of gas-powered devices is not possible. Weatherproof devices are also suitable for outdoor use, as the infrared technology also works independently of environmental influences such as wind. Many models are mounted on the wall or ceiling with a bracket, but floor-standing units are also available.
Electric radiant heaters generate infrared radiation. The heat is felt quickly because the units reach their operating temperature quickly. Although they are less powerful than gas-powered radiant heaters, they convert energy into heat more efficiently. This is why an electricity-powered radiant heater is cheaper to run than a gas heater. The gas radiant heater also produces convection heat that simply dissipates in the air.
Pro points
- Suitable for indoor and outdoor use.
- Easy to install
- Wind resistant
- More energy efficient than gas heaters
Drawbacks
- Limited flexibility
- Less power
What you should look for when buying a radiant heater
Both types of radiant heater are available in different versions, so that there is a suitable device for every area of application. The intended location is important for the purchase decision. On a sheltered terrace, even a rather low-powered unit will provide enough heat. On open spaces, a unit with more power is necessary to ensure that it is pleasantly warm.
Floor-standing unit or fixed installation?
Floor-standing units are often called mushroom heaters because of their characteristic design. Here, the burner is located in the head of the unit and heats a surrounding perforated plate. The screen that sits on the head directs the heat downwards so that it is not lost directly upwards. In addition to the classic mushroom shape, modern floor-standing radiant heaters offer a wide variety of shapes: cone, column or pyramid shapes are now just as common. These devices are often waist-high and therefore more space-saving than a two-metre-high mushroom heater. Electric-powered devices are usually designed for mounting, but there are also models with a stand that can be placed as flexibly as the cable allows. However, such a tripod is significantly less stable than a cone- or mushroom-shaped radiant heater.
Electric heaters are often designed to be mounted on the wall or under the ceiling. Gas mushroom heaters are completely unsuitable for such mounting. Therefore, if you want to mount a radiant heater on the wall or ceiling, you must choose an electric device. Mounting on the ceiling above the area to be heated is the optimal solution in terms of heat distribution. Models with adjustable inclination can be better aligned with the area to be heated.
Power
The ability of a radiant heater to sufficiently heat a room of a certain size depends on its output. For electric radiant heaters, the power is specified in watts, for the more powerful gas radiant heaters in kilowatts.
However, the wattage does not directly indicate how many square metres can be effectively heated with a device. The perceived temperature is influenced by the weather. If your terrace or balcony is very susceptible to wind, you need a radiant heater with more power. A rule of thumb for electric radiant heaters is that a unit with 1,000 watts of power will heat about 4.0 square metres indoors, but only 2.5 square metres outdoors. For an 8.0 square metre patio, you therefore need an electric radiant heater with 3,200 watts. Commercially available, electrically operated radiant heaters have an output of up to 4,000 watts.
Gas-powered radiant heaters for private use have an output of up to 14 kilowatts, i.e. 14,000 watts. A gas radiant heater with an output of 8 kilowatts can heat an area of between 7 and 15 square metres, depending on the location and weather. For large terraces and gardens, a gas radiant heater with up to 12 kilowatts of power should be used.

Operating aspects
Electric and gas radiant heaters also differ in handling due to their different designs. Since a gas-powered unit does not have a power connection, you will find different operating elements than on an electricity-powered model. Electric heaters often have the following elements:
Display: some electric radiant heaters have a screen that provides information about the temperature, time and active settings.
Remote control: To change settings or switch off the radiant heater, the user must go to the unit in models without a remote control. With a remote control, the radiant heater can also be operated from a distance.
Thermostat: Since the surfaces that are heated by the infrared radiation in turn emit heat to the air, the room also heats up. High-quality models are equipped with a thermostat that switches the device off as soon as a certain temperature has been reached.
Rotating function: Some electric radiant heaters have a rotating function, also called oscillation. The radiant heater then slowly rotates back and forth, distributing the heat evenly in the room. This function can usually also be deactivated.
Tiltable head: This is an important feature for radiant heaters that are to be mounted on the wall or ceiling. The heating panel can be tilted and adjusted to the most favourable radiation angle.
Gas radiant heaters have features that are primarily intended to make it easier to handle the heavy gas cylinder and to transport the large appliance. A high-quality gas-powered unit is equipped with the following components.
Piezo ignition: With the help of such an ignition mechanism, the flame can be ignited at the touch of a button. If there is no piezo ignition, the user must ignite the gas himself with a lighter. There is an increased risk of burns when doing so.
Operating hatch: Before each use, it is necessary to open the valve of the gas bottle. After use, it must be closed again. An operating hatch allows direct access to the valve. Without it, the entire housing would have to be lifted each time.
Castors: A great advantage of gas radiant heaters is their flexibility.However, units with a gas bottle inserted have a high weight. To ensure that the heaters are still transportable, many manufacturers equip their units with castors. They can then be tilted and rolled to the desired location.
IP protection class
You can tell whether an electric radiant heater is suitable for the intended location by the IP protection class. IP stands for “International Protection” and is an international industry standard for electrical appliances. The two numbers tell you how resistant a device is to dust and water. The first number indicates the dust protection, the second the protection against moisture. The higher the number, the better the appliance is protected. How high the degree of protection must be depends on where the radiant heater is used. On the terrace, it is not only exposed to moisture, but also to foreign bodies whirled up by the wind. It is therefore essential to pay attention to the manufacturer’s specifications.
| First digit | Degree of protection | Second digit | Degree of protection |
| 0 | No protection | 0 | No protection |
| 1 | Protection against large solid foreign bodies | 1 | Protection against dripping water |
| 2 | Protection against medium solid foreign bodies | 2 | Protection against dripping water at 15 degrees enclosure inclination |
| 3 | Protection against small solid foreign bodies | 3 | Protection against spray water |
| 4 | Protection against granular solid foreign bodies | 4 | Protection against splashing water |
| 5 | Protected against dust | 5 | Protected against water jets |
| 6 | Dust-tight | 6 | Protection against strong jets of water |
| 7 | Protection against temporary immersion | ||
| 8 | Protection against permanent immersion |
An electric radiant heater with IP65 protection is dustproof and can withstand water jets. Consequently, it can be installed without problems in outdoor areas such as a balcony or terrace. A radiant heater classified as IP55 is also suitable for outdoor use. However, it should not be installed in a hobby room where wood is worked on, for example, as it is not dust-proof. A radiant heater with IP22 protection is still suitable for a covered outdoor area, but is more recommended for an indoor space.
Safety aspects
Electric and gas radiant heaters generate high temperatures – the latter with an open flame. This means that there is always a certain fire risk associated with their use. Manufacturers therefore equip their appliances with protective functions to prevent not only fires but also electric shocks and explosions.
A protective grille in front of heating rods and flames is the rule for both gas- and electricity-powered radiant heaters. This prevents direct contact with the heating elements and protects them. Nevertheless, caution is advised because the protective grille also heats up.
With floor-standing appliances, there is always a risk of them tipping over. To prevent this, many units are equipped with a heavy base that can withstand gusts of wind and vibrations. In some designs, the base can be filled with water to weigh down the spotlight. Some units have a special feature: protection against tipping over. A sensor registers the tilted position and automatically switches off the radiant heater at a certain angle.
Electric radiant heaters usually have overheating protection. If the built-in sensor registers that the heating element is heating up too much, the power supply is interrupted.
Many current-operated radiant heaters have an overload protection. This switches the unit off if too much or too little current flows, as this can cause the heating element to become defective.
When buying a radiant heater, it is generally advisable to look for the GS mark or the TÜV seal. A model with such a seal has been tested for safety by an independent testing centre.
Frequently asked questions about the use of radiant heaters
The basic principle of radiant heaters is simple. However, due to the large amount of heat generated, some questions arise, for example, how close you can get to the device and whether it is also suitable for use at the changing table.
How hot can a radiant heater get?
How hot a radiant heater can get depends on the type of device and its output. On average, radiant heaters reach temperatures of 120 to 180 degrees Celsius. Some units can even reach 900 degrees Celsius directly at the heating element. Because of these temperatures, radiant heaters are always equipped with a protective grille or window. Users should try to keep one metre away from the radiant heater at all times.
What are the safety rules for use?
Due to the large amount of heat generated, there is always a certain risk associated with using a radiant heater. There is a risk of fire and burns if the heater is not handled properly. Therefore, pay attention to the exact safety instructions in the supplied instructions for use. In addition, you should follow a few basic rules.
Make sure that there are no flammable objects in the immediate vicinity of the radiant heater. This includes tablecloths, napkins, plants and wooden objects. If possible, clear the immediate vicinity of the appliance.
When connecting an electric radiant heater, do not use multiple sockets or extension cables with a reduced conductor diameter. A small cross-section can lead to excessive heating of the cable. Wiring through a multiple socket can trip your home’s main fuse or, in the worst case, cause a fire.
For reasons of stability, always place a gas heater on a level surface. Ensure that there is a sufficient supply of fresh air and never operate such a device in a closed room. Check which minimum distances to combustible components such as awnings are recommended in the instructions for use. The ventilation openings of the radiant heater must not be covered.
What can a radiant heater be mounted on?
A bracket is usually included with wall and ceiling radiant heaters. The material on which the radiant heater is mounted must be able to bear the weight on the one hand and must not be damaged by the radiated heat on the other. Safe surfaces for mounting are walls and metal. Wood is not recommended and plastic surfaces are not recommended at all. The backs of the units also become very warm during operation. If the heat accumulates, a fire can occur in the worst case. For this reason, the radiant heater should always be mounted at a sufficient distance, even on safe surfaces such as brickwork.
Is a radiant heater useful at the changing table?
It can happen at any time of day or night that a baby needs to be changed. The room with the changing table is not always properly heated, for example shortly after airing the room. Then the baby can quickly become hypothermic. Babies do not yet have a fully developed immune system and are therefore susceptible to illnesses such as colds. An electric heater above the changing table that provides direct heat helps out here.
For the child’s safety, make sure that the radiant heater is explicitly designated for use at the changing table. An electric radiant heater designed for outdoor use is probably unsuitable. Some manufacturers explicitly advise against using it when changing nappies.
















 238 reviews
238 reviews




