Office chair purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- What You Need to Know
- A good office chair supports the user in healthy, dynamic sitting.
- It is crucial that the chair can be adjusted to its user.
- A good mechanism promotes movement when sitting.
- You can’t sit well on a bad chair, but having a good chair doesn’t automatically mean you’re sitting correctly.
- In addition to ergonomics, build quality and design are important buying criteria.
- The wrong casters can damage the floor.
Sitting: Epidemic and achievement
Many people spend a great deal of their time sitting. Even schoolchildren are encouraged to sit still during lessons. Later, it is the daily work routine, which for the majority of the population consists of sedentary activities. This has unpleasant consequences. Frequent and, above all, incorrect sitting can lead to a whole range of illnesses and problems, from posture problems to chronic back pain to slipped discs. A typical consequence of incorrect sitting is the “computer hump”, the typical lowered and protruding head of computer screen workers, which not only looks unattractive, but also leads to extremely unpleasant tension in the neck and headaches. Frequent sitting has even been linked to incontinence, heartburn and diabetes.
The right office chair significantly reduces the individual risk of many of these problems. On the one hand, it relieves pressure on the body, and on the other, its design encourages frequent changes in sitting position. Both are important in preventing possible damage from prolonged sitting.
How much time do we spend sitting?
According to a 2016 study by health insurer DKV, every German spends an average of seven hours a day sitting. Office workers even spend an average of eleven hours. Sitting incorrectly is one of the main causes of back pain, from which 43 percent of all working people suffer.
People need to sit
However, the ability to sit properly is extremely important for us humans. In no other body position can we concentrate on our environment as well as when sitting, while the body is comparatively relaxed. It is difficult to imagine working attentively on a task for a longer period of time while standing or lying down. So you can’t do it without sitting. That makes it all the more important to sit correctly. With this in mind, take a seat, make yourself comfortable and let us tell you how the right office chair can increase your sitting comfort and help you avoid the harmful long-term effects of your sedentary work.
Designs of office chairs
Generations of engineers and designers have worked to create the perfect chair. Even office chairs have developed a few basic shapes over time, from the simple office swivel chair to the comfortable executive chair to chairs created specifically to meet the needs of gamers.
The simple swivel chair
The simplest variant of an office chair is the simple swivel chair. It is often found in private households. Especially in children’s and young people’s rooms, this furniture is often found. Pupils take a seat in it to do their homework. Usually it consists of a base on which a height-adjustable seat shell with a backrest is mounted. A rocker mechanism is usually missing, and armrests are often omitted as well. The back support is usually only half-height, so that support for the spine in the back area is not guaranteed. Retailers have a lot of fashionable designs on offer, aimed at consumers who do not want to create an office atmosphere at their home office, which is only used occasionally.
The executive chair
A thickly upholstered executive chair offers much more comfort than an ordinary desk chair. It is a good choice not only for bosses, but for everyone who spends several hours a day sitting at their workplace. Visually, executive chairs usually look rather serious. Unlike swivel chairs, models in bright colors or with eye-catching patterns are hardly available. The seat and backrest of executive chairs are often upholstered with artificial leather and, in the case of particularly high-quality models, even with genuine leather. It goes without saying that the seat is height-adjustable thanks to a gas pressure spring; in addition, there is usually also an adjustable backrest and adjustable armrests. The backrest reaches up to the shoulders, and often there is also a built-in headrest, which provides valuable services, especially in models that tilt far back.

The gaming chair
As the name suggests, gaming chairs are not actually intended for office work at all, but for playing computer games. However, the requirements are similar. Both activities are about making long periods of sitting in front of the computer as comfortable as possible. That’s why office workers have also discovered gaming chairs for themselves. Basically, they are very similar to classic executive chairs, but they differ in design. The design of gaming chairs is more sporty than classically elegant. It borrows from the seats of racing cars, which is why computer chairs are also called racing chairs. Even the shape is reminiscent of car seats, and the usually two-tone design underscores the sporty look.
Gaming chairs often have a backrest that can be folded almost horizontally and an extendable footrest. This also distinguishes them from executive chairs. The designers of seating furniture primarily intended for work shy away from such concessions to comfort. Gaming chairs, on the other hand, are leisure furniture; they can and should be comfortable.
The ergonomic or orthopedic office chair
Strictly speaking, every office chair should be ergonomic, i.e. it should optimally support the user while sitting during office work. However, orthopedic or ergonomic office chairs are mainly sold as models that can be adapted to individual requirements to a particularly large extent. Not only the seat height is adjustable, but usually also the height and sometimes even the tension of the lumbar support, the tilt angle of the backrest and seat, and the armrests. It is advisable to get help from an ergonomics expert when setting up such a chair for the first time. This is especially true if, but not limited to, the user is already suffering from illnesses due to improper sitting. Anyone suffering from serious musculoskeletal conditions, such as a herniated disc, should discuss their choice of office chair with doctors and therapists anyway.
The office stool
Roll stools are mostly used by people who want to be as mobile as possible while sitting. They are often found in hairdressers, tattoo artists, physiotherapists and doctors. The stool is out of the way when working with customers or patients, yet provides them with a place to sit so they don’t have to spend their long workdays standing. Stools also have their fans among workers in offices. After all, they restrict movement less than chairs with backrests and armrests and thus promote dynamic sitting with frequent changes of position, which is considered healthy.
In the absence of a backrest, the sitter must keep his or her upper body upright under his or her own power, which strengthens the torso muscles, which in turn are important for a healthy sitting posture. However, sitting on a stool without a backrest is also strenuous. Especially when working for long periods of time, many people therefore tend to adopt an unhealthy, slouched sitting posture on a stool, with the pelvis tilted back and the cervical and shoulder vertebrae rounded forward – the typical screen posture.
Design and operation of office chairs
Some office chairs look like small machines. With levers and knobs, they seem to have sprung from the mind of an engineer rather than a designer, and in fact many specimens have some technical refinements that clearly distinguish them from ordinary kitchen or visitor chairs. What is a typical office chair made of, what can it do, and what use are the individual adjustment options?
Caster castors
In order to move the office chair, its feet are equipped with casters. These are not just any castors, but so-called caster wheels. The alternative name caster wheels makes it clear what their special feature is. Unlike simple fixed castors, they are suspended on the vertical axis so that the chair can roll in any direction. They usually also have a second special feature: they only roll when the chair is loaded. On the other hand, if no one is sitting in the office chair, they are braked with the help of a special mechanism. This prevents accidents that occur when the chair rolls away during sitting down.

The castors of office chairs are interchangeable and should be chosen to match the floor covering. For hard floors such as wood or laminate, soft casters are available that are gentle on the flooring and prevent the chair from rolling too fast due to their increased rolling resistance. For carpets and rugs, on the other hand, hard casters are recommended. They reduce the increased rolling resistance on these floor coverings, and in addition, no fibers stick to the hard plastic and are pulled out of the floor covering, as sometimes happens with soft castors, especially on hot summer days.
Foot cross
The base forms the basis of the office chair. In old specimens, it was often four-armed, but today, for reasons of stability, it usually consists of five or even six arms. Plastic is often used as the material for inexpensive models, while higher-quality models have a base made of steel or aluminum. Plastic base crosses tend to show signs of wear. It can often be observed with them that the spring sags to the floor after a long period of use. The metal version is much more durable.
Seat
Besides the backrest, the seat is the part of the office chair that has the most contact with the body. Its design, therefore, contributes significantly to the ergonomics and comfort of the chair. It should be deep enough so that the user still has a little space between the front edge of the chair and the back of his knees when he slides all the way back in the chair. The width should be such that the sitter is not cramped and the arms can rest comfortably on the armrests. Depending on the user’s physical conditions, an office chair is ideally between 40 and 50 centimeters wide.
The seating position should be adjustable so that the seat slopes slightly toward the front. This results in a greater angle between the pelvis and thigh when sitting, which is ergonomically favorable because it ensures better blood circulation and makes it easier to avoid a hunched back. The front edge of the seat should be slightly rounded so that blood circulation to the lower legs is not disturbed by a sharp edge.
Mechanics
A rocking mechanism in an office chair encourages dynamic sitting with many small changes in posture throughout the day. Individual manufacturers use a myriad of different mechanisms that differ in details, but they can all be traced back to four basic types: Rigid permanent mechanism, rocker mechanism, synchronous mechanism and anynchronous mechanism.
Rigid mechanics
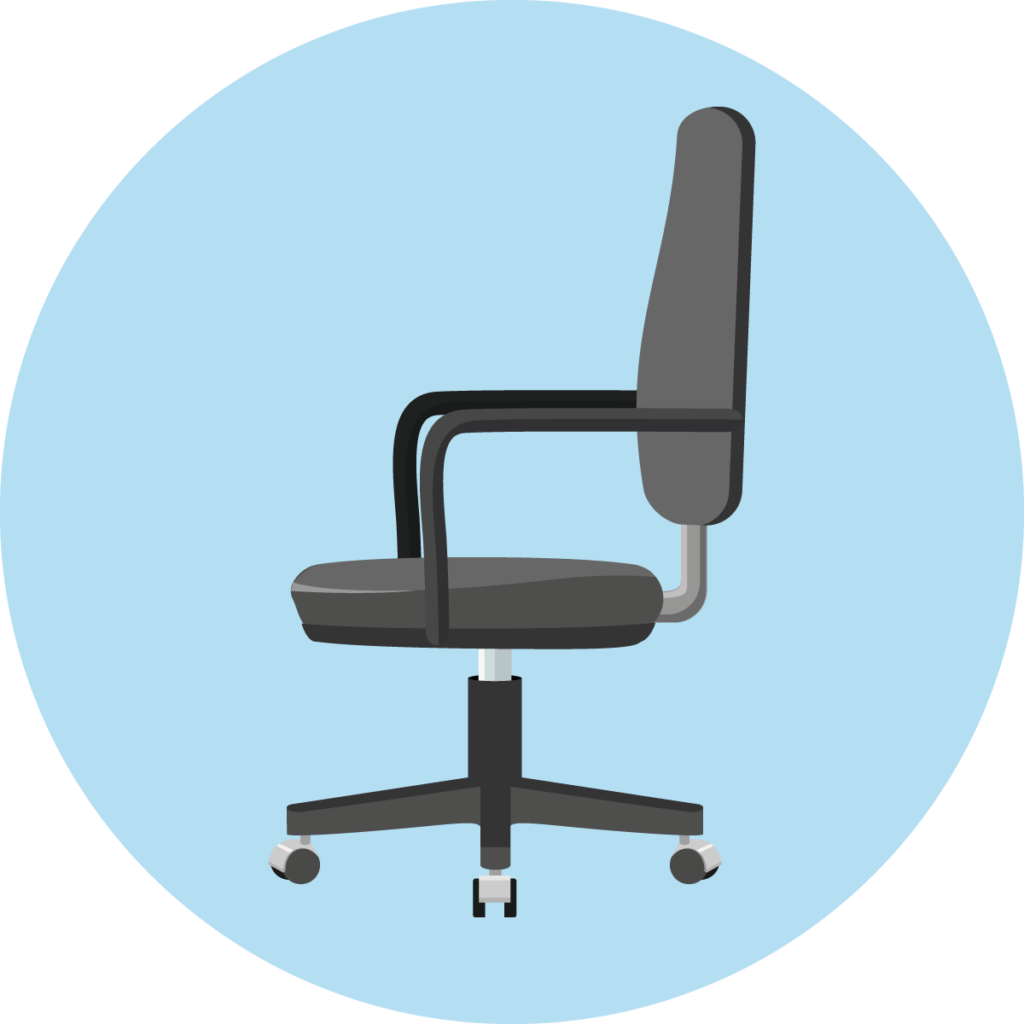

In a chair with a rigid mechanism, neither the seat nor the backrest is movable. Such office chairs are mainly found in the lower price segment. Many office chairs with retro design also have a rigid mechanism, as they forgo sophisticated construction in favor of looks.
Permanent contact
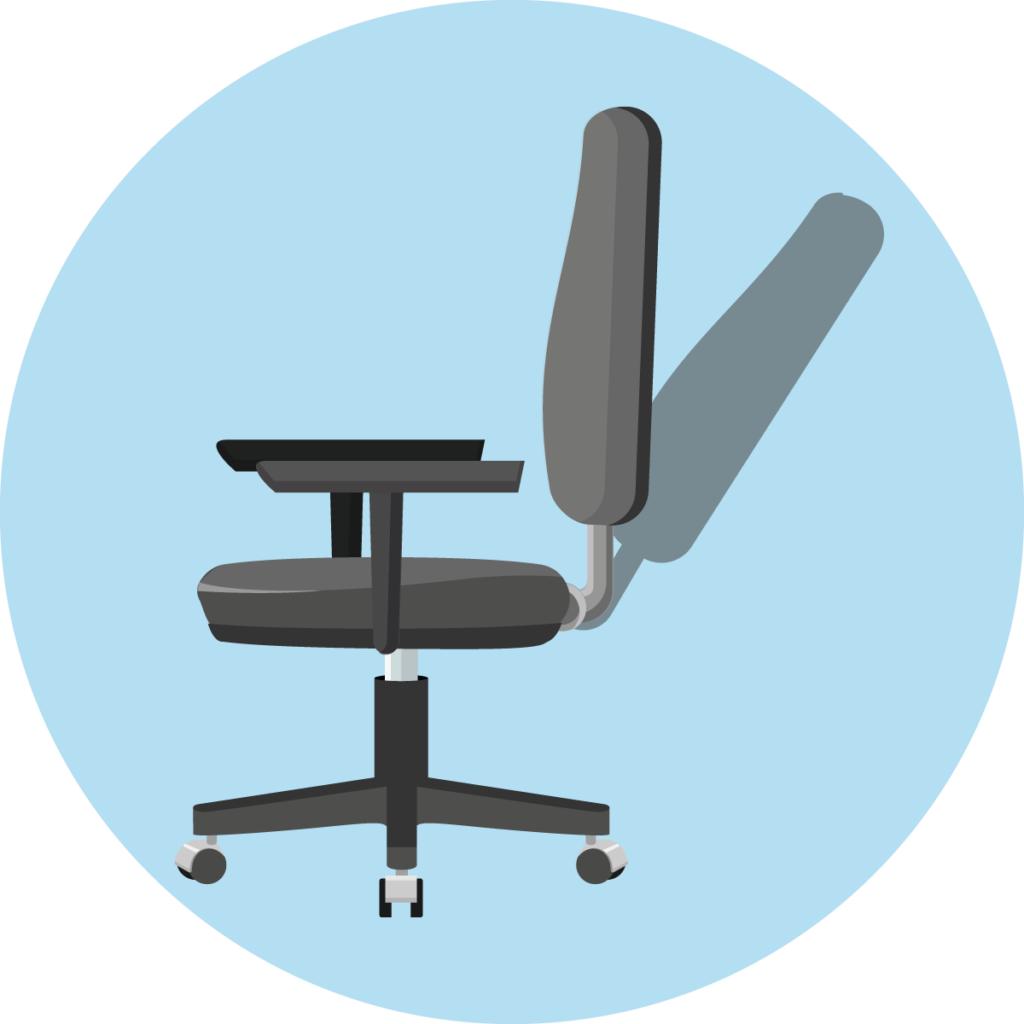

In an office chair with permanent contact mechanism, the seat is rigid, but the backrest yields and exerts a springy pressure on the back. Thus, it does not lose contact with the back either when sitting upright or when leaning back. If you don’t want that, you can also lock it in a reclining position that is comfortable for you.
Rocking mechanism
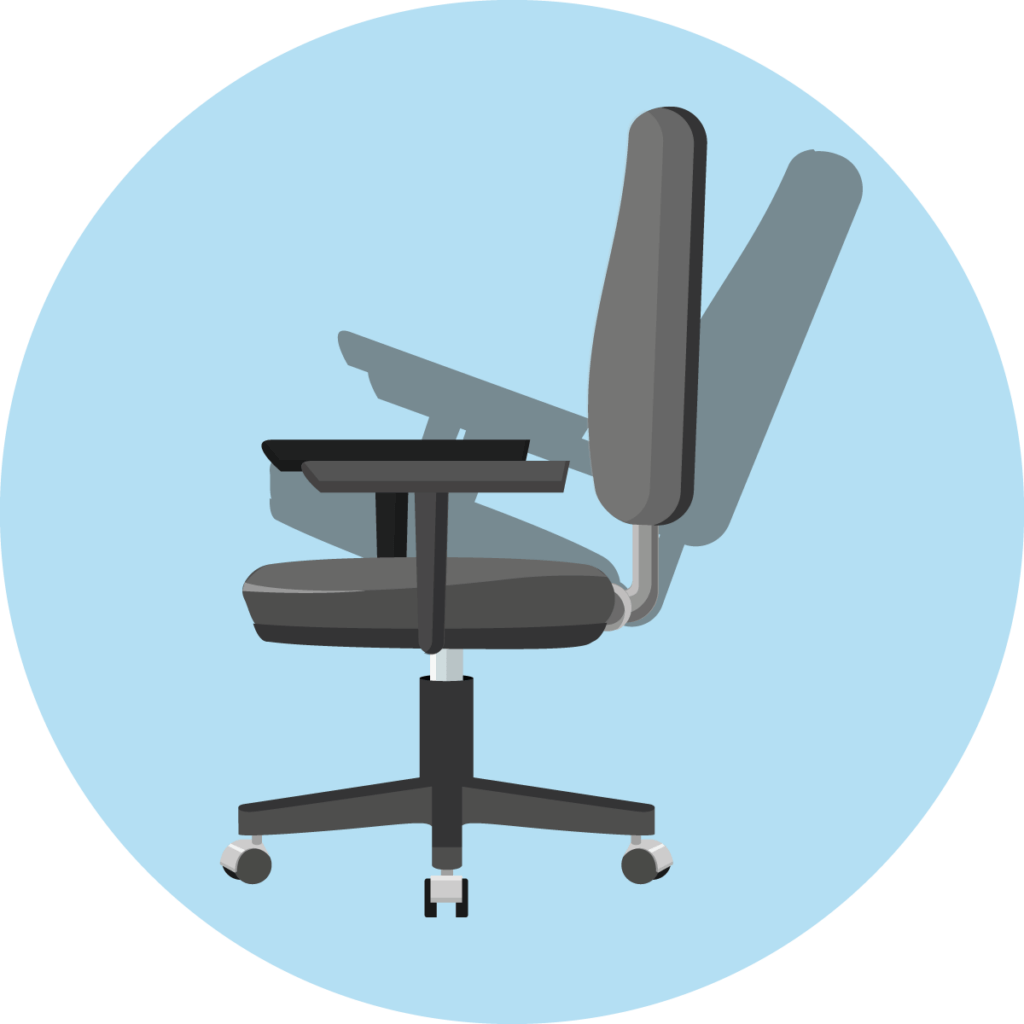

If the office chair has a rocking mechanism, the seat and backrest form a unit that moves together. Similar to a rocking chair, the user can rock back and forth, but the angle between the thighs and upper body always remains the same. The rocking mechanism is the classic mechanism of executive chairs.
Synchronous mechanism
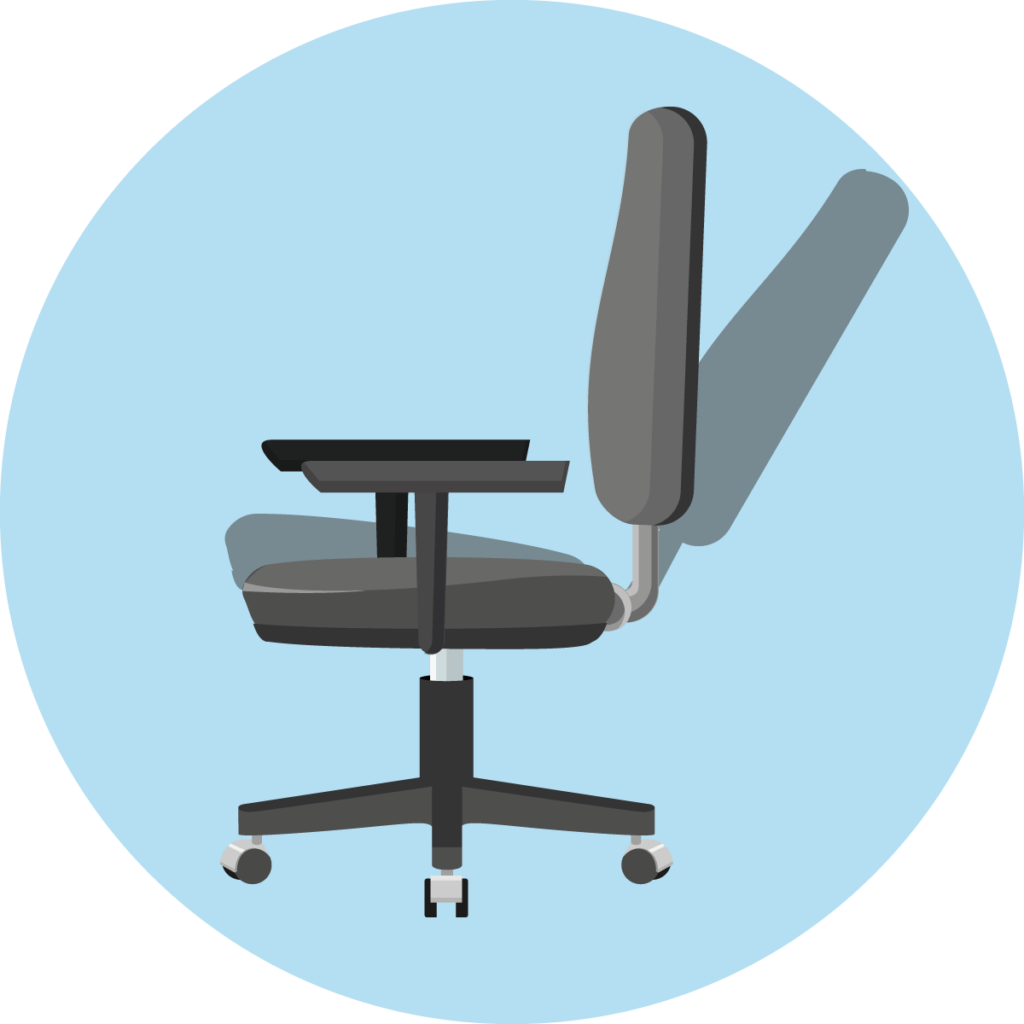

The most sophisticated mechanism that an office chair can have is the synchronous mechanism. With this mechanism, both the seat and the backrest move when the user reclines. Unlike the rocker mechanism, however, they do not form a single unit, but move differently. The backrest moves more than the seat. This results in the user adopting a sitting position with a greater angle between the upper body and thighs when leaning back. This facilitates blood circulation and is ergonomically beneficial overall.
Backrest
The backrest of an office chair should be high enough to support the body up to the neck when sitting. It is important that the top edge is soft and rounded towards the back, otherwise it will exert painful pressure during prolonged sitting. In the lumbar region, most backrests are curved a little forward, with this shape they follow the natural curvature of the spine. The forward curved part of the backrest is called the lumbar support. Ideally, its height can be adjusted separately. A headrest or neckrest can be dispensed with, but many users find it very comfortable, especially in a reclined sitting position.
Armrests
Armrests not only provide support when sitting, but also make it easier to sit down and stand up. Ideally, they allow the user to lower their spine onto the seat surface without impact when they sit down. To provide optimal support when sitting, armrests should at least be height-adjustable. It is even better if they can also be swiveled and adjusted in depth.
Cover
The cover of an office chair is not only important for its appearance, but also has an impact on seating comfort, maintenance requirements, durability and, last but not least, price.
Genuine leather
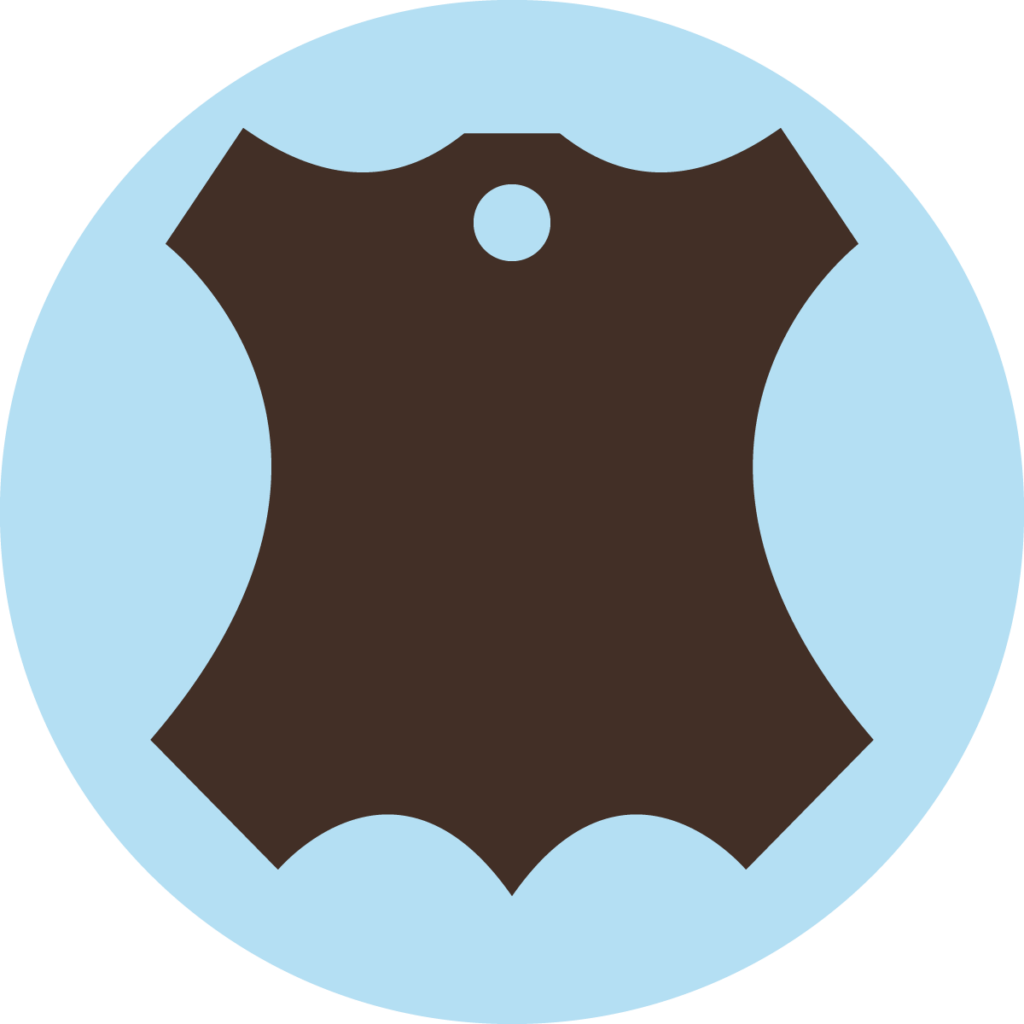
Genuine leather is a high-quality natural material and has very advantageous properties for office chairs. It is pleasant to the touch and breathable, in addition, stains can be easily wiped off, and with good care it is durable for a long time. But the downside is that leather is by far the most expensive option in covers for office chairs. For some models, the price difference between the textile and leather versions is one hundred euros or more.
Imitation leather

Visually, imitation leather can hardly be distinguished from real leather, and it is also significantly cheaper. But that’s where the advantages of this material end. Since it is hardly breathable, sweat is not dissipated, which can be very unpleasant, especially on hot days. In addition, artificial leather is much less durable than genuine leather. While the original forms a visually appealing patina over time, faux leather flakes off and becomes brittle, making older faux leather covers quickly look shabby.
Textile
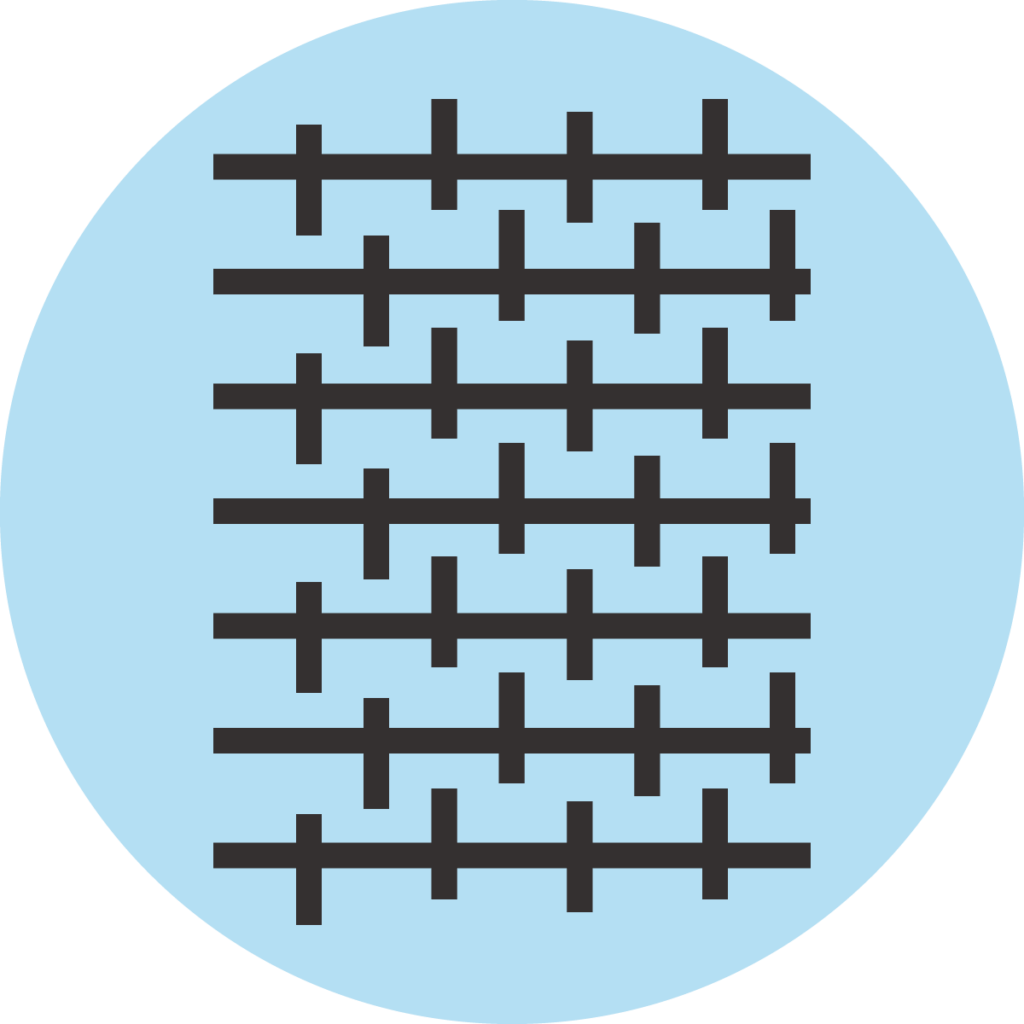
Textile covers come in a number of varieties. Retailers offer covers made of natural fibers such as linen or cotton, as well as those made of synthetic fibers such as viscose and polyester. They are usually relatively cheap, cheaper even than artificial leather. The main disadvantage of fabric covers is that they are difficult to clean. If you like to eat at your desk and tend to spill, it’s better to choose a different material.
Mesh
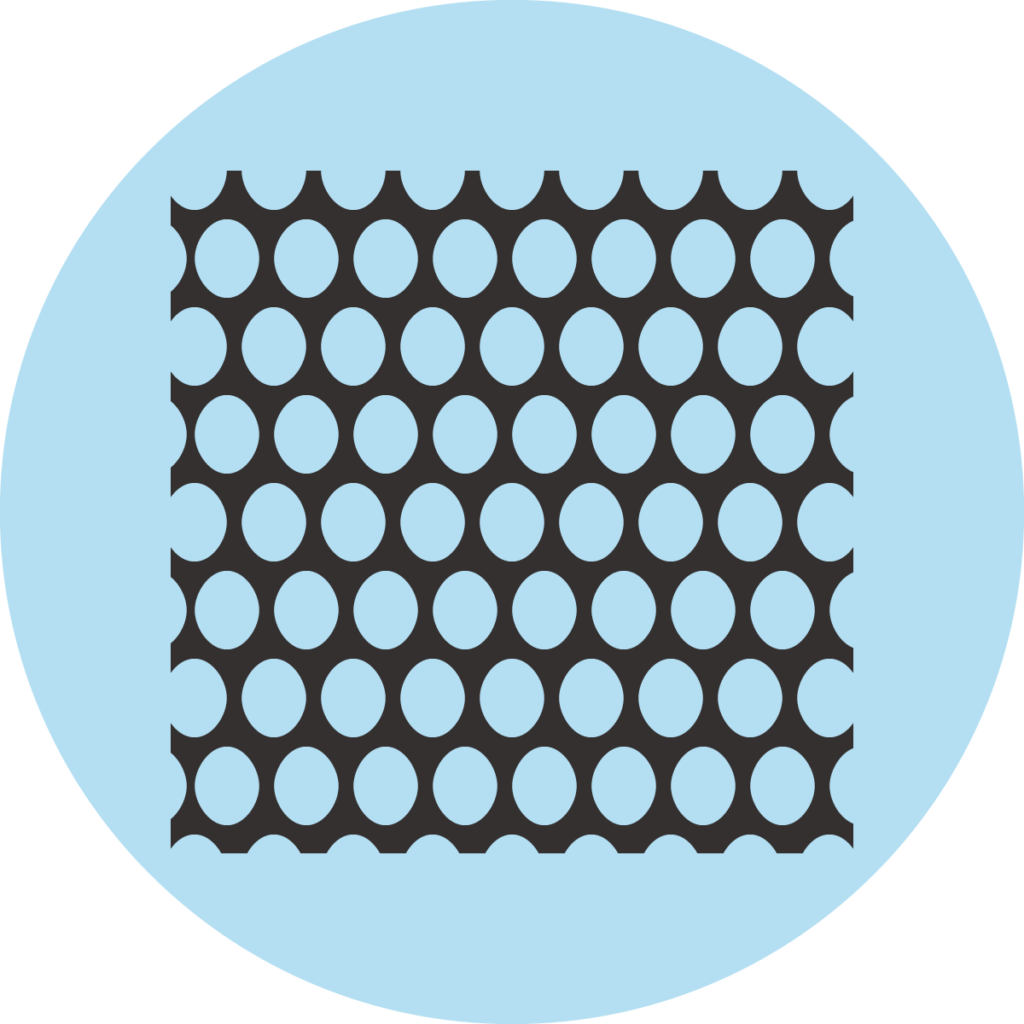
Usually only the back of office chairs is made of mesh, but there are exceptions, such as the classic Aeron by manufacturer Herman Miller, where the seat is also covered with mesh. Mesh is a thin net made of plastic fabric (rarely metal) that combines good air permeability with high flexibility. Since mesh backrests require less material than upholstered versions, chairs with mesh backrests can also be found in the lower price segments.
Operability and function levers
Most office chairs have at least two functional levers: one for adjusting the seat height and one for locking the mechanism. The lever for the seat height is almost always located on the right under the seat and can be easily reached with the right hand. The locking lever is located in different places. Some manufacturers also combine the two levers. In addition, office chairs have various adjusting screws and other adjustment options, for example, to adjust the lumbar support or change the resistance of the mechanism. All these controls should be easy to reach and operate without tools.
Load capacity and maximum recommended sitting time
Manufacturers provide information on the maximum load capacity for virtually all available office chairs. This figure indicates the maximum weight a person should have when sitting in the office chair. The majority of office chairs for adults have a maximum recommended load capacity of more than 100 kilograms, so they can be used by most people without any problems. Only office chairs for children and teenagers have lower load limits.
Another specification that manufacturers sometimes make is the maximum recommended daily sitting time. For task chairs, it should be at least eight hours. If the chair is used only occasionally at home, a lower value is also acceptable.
What accessories are useful?
There are not too many useful accessories for office chairs. If you look for them in online shops, you’re more likely to find spare parts: Gas struts, foot crosses, chair mechanisms or complete bases are available. They are mainly meant to repair damaged office chairs. If there is no defect, it may make sense to replace the casters in some circumstances. Some users may also want to add armrests or a headrest to their office chair. Regular rolling back and forth can also damage laminate and hardwood floors in the long run, so a floor protection mat is a good idea.
Castors and floor glides
Office chair casters are very easy to replace. All you have to do is release them from their anchorage with a little pull and insert the replacement castor into the anchorage with light pressure. It then engages with a clicking sound. So if you want, you can change your chair’s standard casters for one of the many available varieties. Common office chair casters are divided into hard floor and soft floor or carpet casters. Hard floor casters have a relatively soft surface so as not to leave scratches on the flooring. Carpet rollers, on the other hand, are hard to prevent fibers from sticking and to keep rolling resistance low. They can usually be identified by their color: while carpet rollers are entirely black, hard floor rollers have a light outer layer of rubber.
If you want to “tune up” your office chair a little, you can install narrow, single casters instead of the usual double office chair casters. These are reminiscent of the rollers on rollerblades. They are narrower and higher than usual office chair castors. In addition, they are also smoother, quieter and particularly gentle on the floor. However, the disadvantage of this sporty variant is that, unlike usual office chair casters, they do not brake when the chair is not loaded. As a result, the chair may roll away in the event of a slight impact while sitting down and the user may sit down in the void. In other words, they increase the risk of accidents.

If you want to prevent your office chair from rolling away altogether, you can use plain floor glides that can be inserted into the holes provided for the casters. This is useful, for example, if the floor is uneven. Floor glides are also a good solution for users for whom protecting the floor covering is more important than the mobility of their chair.
Floor protection mats
Another way to prevent floor damage from rolling back and forth with an office chair is to use floor protection mats. These usually transparent plastic mats, similar to casters, are available in designs for carpet or for hard floors. Universal mats are also available. An important factor in the quality of the mat is its thickness. Cheaper mats are only about half a millimeter thick and thus look more like foil, while robust versions have a thickness of up to one and a half centimeters. The mats are available in different sizes. When deciding on the right size, the rule is: if in doubt, go a little bigger. Because it can happen all too quickly that the user rolls over the edge of the floor protection mat with the chair and scratches his floor covering as a result.
Armrests and headrests
Armrests and headrests are optional on many office chairs. At the time of purchase, the customer has the choice of whether or not to include these accessories. Usually they are also available separately, and he can reorder them later. But be careful, usually only the original accessories fit. So a desk chair from Songmics, Topstar or HJH Office necessarily needs the manufacturer’s accessories. No one should do without armrests; they are important for a relaxed posture when working. Headrests, on the other hand, are a matter of taste; they are only of real benefit in a reclined sitting posture.

Protective covers
A variety of covers made of stretchable fabric are commercially available to fit a wide range of office chairs. A removable and washable fabric cover protects against contamination and, especially important with synthetic leather, wear and tear. In addition, these protective covers are a simple way to spruce up an old office chair that has become unsightly.
Sitting correctly
A good office chair helps its user sit properly. But how do you sit properly? On the one hand, it is important to set up the workstation in such a way that the body is not forced into stressful incorrect postures when working at the desk. On the other hand, you have to sit in such a way that the body’s movement and support apparatus is not overloaded. What may come as a surprise to many: There is no such thing as the one optimal sitting posture. The healthiest way is to vary your sitting position as often as possible. Experts call this dynamic sitting. After all, sitting correctly is above all a headache – you shouldn’t just rely on a chair that bends you over.
Setting up the workstation
The basic prerequisite for healthy sitting is the correct furnishing of the workplace. If things like the seat height or the distance to the monitor are not right, it is difficult to adopt a good sitting posture.
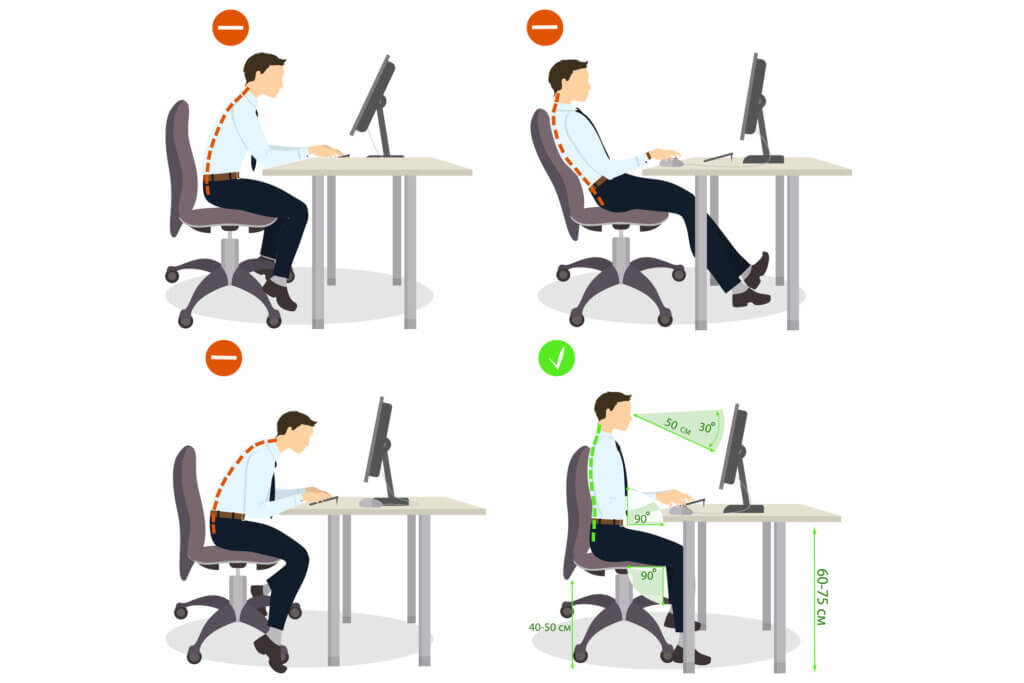
1. adjust the seat height correctly
The seat height should be adjusted so that the knees have an angle of at least 90 degrees. If the seat is too high, the edge of the chair presses against the thighs; if it is too low, an acute angle is created between the upper and lower legs when the thighs are positioned vertically. Both restrict blood circulation, which is unfavorable in the long run. There is also a risk of shortening the hip flexors. These are the muscles that keep the hip mobile. When they are shortened and lack suppleness, they force the spine into a harmful posture. For short people, it makes sense to use a footrest instead of setting the chair lower, because otherwise the monitor and keyboard would be positioned much too high on a table without height adjustment.
2. set the seat at an angle
The seat should be adjusted so that it is slightly tilted forward. This helps the sitter to sit with the pelvis tilted slightly forward. This is important because sitting with the pelvis tilted backward automatically leads to a hunched back, which is harmful to the spine in the long run. If the seat cannot be tilted, wedge-shaped seat cushions for office chairs can be used, which are available in the trade for this purpose.
3. position the monitor correctly
The screen is positioned correctly when it is about an arm’s length from the body. The top edge of the screen should be at eye level so that the head does not have to be lowered when working, which would cause tension in the neck muscles. If the screen is not height-adjustable, the user can help himself by placing it on a stack of books. A laptop should also be adjusted to the correct height for constant use. To be able to use it comfortably even then, an external keyboard and mouse are necessary.
Sitting in a healthy position
A correctly set up workstation is the basic prerequisite for correct sitting, but the fact that the table, chair and monitor are ergonomically optimal does not guarantee good posture. A basic knowledge of work ergonomics is necessary to avoid harming your body in the long run.
1. sitting backwards on the chair
It is not advisable to sit at the very front of the chair. The reason for this is that then only a few support surfaces bear the entire body weight and the muscles are loaded on one side to keep the body upright. With a position at the very back of the office chair, on the other hand, the backrest also contributes to keeping the body upright. The body weight rests not only on the buttocks, but also on parts of the thighs. Since the support surface is larger, there is less pressure on the parts of the body that are in contact with the chair.
2. sitting upright
VDU workers tend to adopt a forward-curved posture, which places a very uneven load on the intervertebral discs. In addition, the back muscles are almost solely responsible for maintaining the body in this position, whereas in an upright sitting position, the abdominal and chest muscles also bear an important part of the load. A bent posture also constricts the internal organs and the higher pressure on the thighs worsens the blood circulation in the lower extremities. However, it is difficult for untrained people to sit with a straight back for a long time. They will find it easier if they lean against the backrest and adjust the seat so that it leans slightly forward.
3. use armrests, palm rests and footrests
The idea behind armrests and palm rests is a simple one: the more support surface the body has, the less pressure there is at the points of contact and the less work has to be done by muscles that aren’t designed for one-sided strain and don’t cope well with staying in one position for long periods of time. Armrests relieve pressure on the shoulder area, and palm rests prevent the wrists from either bending unnaturally from resting on the table or from constantly straining the arms, as is the case with a floating typing posture.
Dynamic sitting
The human body is not made to remain in the same position for long periods of time, as is the case when sitting. In order for muscles, tendons and joints to remain healthy, they need to be moved. Getting up as often as possible in the office, for example for standing meetings or to go to the printer, is therefore healthy. The ideal solution would be an adjustable standing desk, which would allow workers to spend part of the day standing instead of sitting. However, most employees are not spoiled with such a luxury. But at least they have the option of sitting as dynamically as possible. In plain language, this means changing the sitting position frequently.
The easiest way to implement dynamic sitting is to alternate between a front, upright and rear sitting posture.
In the front sitting position, the upper body is bent forward slightly so that the forearms rest on the desk. The knees form an acute angle so that they point lower legs slightly backward. The hips and elbows also have an acute angle.
The upright sitting posture corresponds to what is generally considered a good sitting posture. The upper body is kept as vertical as possible, and the knees, hips and elbows are bent at approximately the right angle.
In the rear sitting posture, the sitter is already halfway to a reclining position. He leans the upper body as far back as possible, knees, hips and elbows form an obtuse angle.



















 675 reviews
675 reviews


