Car battery charger purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- What You Need to Know
- Car battery chargers must be compatible with the battery in your car.
- Most chargers are designed for 12-volt lead-acid car batteries.
- Chargers with maintenance mode can keep the capacity of a battery constant over a long period of time.
- Special protection mechanisms, such as short-circuit, overcharge or reverse polarity protection, minimise the risks to the battery, the charger and you.
- First clamp the black or blue cable to the negative terminal and then the red cable to the positive terminal.
Charge and leave
There are only a few minutes left until the appointment, so get in the car, start the engine and go – or not. All too many drivers are familiar with the problem of a flat car battery. The reasons for this can be very different: If you use the rear window and seat heating while driving, for example, this is at the expense of battery capacity; sometimes your own forgetfulness is also to blame. If you forget to switch off the headlights in the evening, you are guaranteed to find a car with an empty battery the next morning. Classic car owners must also expect a discharged battery when they bring the vehicle out of its winter quarters, because even a disconnected battery discharges over time.
Nowadays, recharging the car battery can be done in a few simple steps. Car battery chargers are no longer as bulky as they used to be. With a size of just a few centimetres, they are easy to store and convenient to use. Even the settings often no longer have to be made manually. This takes a lot of the work out of the hands of motor vehicle laymen. All you have to do is connect the charger to the car battery as well as to a power socket and within the next few hours it will be fully charged. Thanks to various protective mechanisms, you are protected against short circuits and flying sparks. An automatic switch-off prevents overcharging and overheating of your car battery. Without this, the battery could be damaged.
High-quality car battery chargers are already available for less than 100 euros. This is basically a sensible investment for every car driver. The compact chargers not only help you in the event of a flat car battery, but also increase the battery’s lifespan by several years.
Pro Points
- For home use
- Handy
- “Intelligent” charging functions
- Integrated protection mechanisms
Drawbacks
- Charging over several hours
- Dependence on a power source
- Danger of overcharging if automatic switch-off is missing
Why is the car battery flat in the first place?
- You left the interior light or the headlights of the car on without moving the car.
- Energy guzzlers such as the heating system require a particularly large amount of electricity in cold winter months.
- If you only drive short distances every day, the car’s alternator may not be able to charge the battery sufficiently.
- The batteries of older cars that are only driven seasonally will discharge themselves over time.
What to look for when buying a car battery charger
When buying a car battery charger, there are comparatively few criteria to consider. First and foremost, the charger must be compatible with your car’s battery. You will find a detailed description of the different battery types below. However, it is not only the type of battery that is decisive here, but also its voltage and the charging current of the device itself. Additional functions and protection mechanisms are usually not essential, but are still recommended to a certain extent.
Eagerly awaited
The output voltage of the battery to be charged is decisive for buying the right charger. Most modern car batteries have a charge of 12 volts. Batteries with twice the charge of 24 volts are fitted in trucks and some motorhomes, while motorbikes get by on 6 volts. However, you should check in advance, as there are also motorbikes with 12-volt batteries and old cars may have a 6-volt battery installed. Some chargers allow you to switch the voltage, which is particularly useful if you have different vehicles, for example a car with a 12-volt battery and a motorbike with a 6-volt battery.
| Motorcycle/scooter | Car | Truck | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery voltage | 6 volts | 12 volts | 24 volts |
The charging current
The current of the car battery charger also depends on the battery of your vehicle. In most cases, the manufacturer of the battery specifies the amperage with which you may charge it. As a rule of thumb, the charging current should correspond to one tenth of the battery’s capacity. A battery with 60 ampere hours should therefore be charged with a charger with 6 amps and a battery with 100 ampere hours with 10 amps. The current rating of most chargers is between 3 and 10 amps. In addition, the charging current is relevant for the charging time: The more charging current, the shorter the charging time.
The charging functions
Admittedly, the additional functions are not elementary to the actual task of a car battery charger. However, the various modes make it easier for you to use them and make the process as simple as possible. For example, some devices recognise when the battery is fully charged and then switch off or change the mode, such as to maintenance mode. Thanks to such “intelligent” behaviour, you do not have to permanently monitor the charging process. A display on the device and possibly integrated LED lights inform you about the charge status of your battery.
Trickle charge function

Thanks to this function, the battery charge level is kept constant at almost 100 percent over a longer period of time. The trickle charge mode prevents the voltage from dropping due to constant charging and is activated as soon as the battery capacity drops below 95 percent. In this way, you prevent a deep discharge of the battery, which in turn has a favourable effect on its longevity. This is particularly useful for vehicles that are only used seasonally.
Recovery function

This function partially restores the capacity of a heavily discharged battery. Batteries that are deeply discharged are usually no longer considered rechargeable. Thanks to this mode, you can still use the battery. This is especially practical if your vehicle remains unused for a long time and you have forgotten to connect a charger with a maintenance function.
Jump-start function

A charger with this function will jump-start the engine immediately after charging. The charger serves as an external power source to supply power to the battery and start the combustion engine with electric starter. The only criterion for this is that the voltage of the battery and the charger must be the same.
Deep, deeper, deeply discharged
When we talk about a deeply discharged battery, this means that the battery is completely empty. Some batteries are considered defective in this state and usually cannot be recharged. Chargers with a special function can revive deeply discharged batteries in many cases, but this results in a loss of capacity.
For the safety of man and machine
The latest car battery chargers have various protective mechanisms that not only protect the battery and the charger itself, but also the user. A charger with these functions is forgiving of possible operating errors and prevents damage to property or personal injury:
- Overheating protection: if the battery gets too hot during charging, the unit switches off automatically.
- Reverse polarity protection: If you reverse the negative and positive poles, this protective mechanism prevents possible damage to the battery.
- Overcharge protection: A unit with this protection mechanism switches off as soon as the battery is charged to prevent overcharging.
- Short-circuit protection: Thanks to this mechanism, the unit and the connecting conductors are protected against impermissibly high currents caused by short circuits.
- Spark protection: This protective function prevents sparks from being generated when a connection is made between the unit and the battery.
The housing
The housing of a car battery charger protects the technology inside the device, which weighs only a few hundred grams. The industry standard today is IP-65, which describes the degree of protection and indicates the suitability of the equipment for various environmental conditions. The number 6 means that the chargers are dustproof and offer full protection against shocks. The digit 5 indicates that the housing is protected against splash and jet water. However, you should not leave the chargers out in the rain.
The cable length
The cable length of a car battery charger is a factor that should not be underestimated. Remember that you need a power outlet to charge your battery. Since there is not always an outlet near your vehicle and the charger may need to be right next to it, a long cable is highly recommended.
The terminals
Car battery chargers are connected to the battery via connecting leads. There are two different types of terminals that are located at the end of the conductors and connect to the battery.
Alligator clips
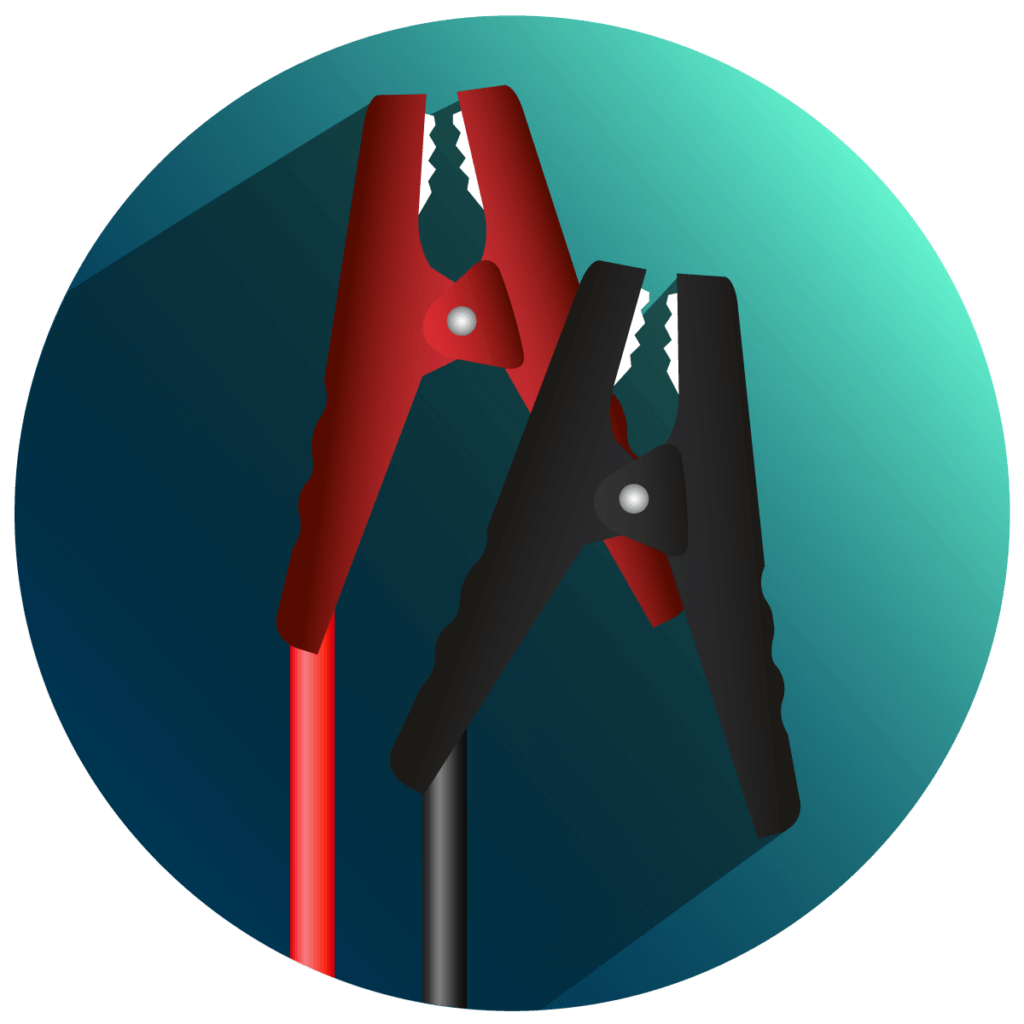

Alligator clips are similar to clothes pegs in the way they work and are clamped to the terminals of the battery. In this way, you make a connection between the charger and the car battery quickly and without the need for tools. However, when buying them, make sure that the clamps can be moved far enough apart. The disadvantage of this method is that the alligator clips sometimes slip off with the slightest vibration. Regular checking of the charging process is therefore recommended.
O-ring terminals
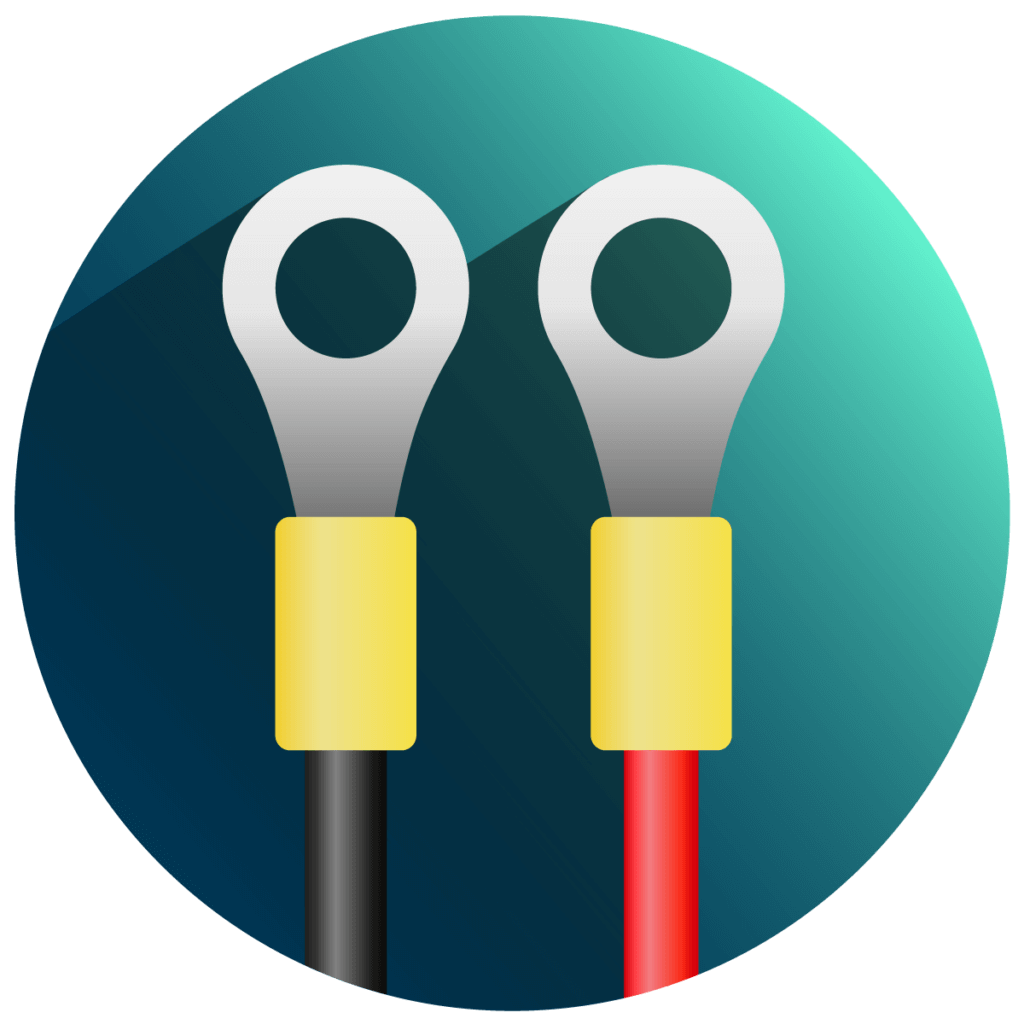

These connecting conductors, also called ring lugs, have circular or ring-shaped connections at their ends. They are plugged into the terminals of the car battery, creating a connection between the battery and the unit. O-ring terminals are intended for long-term use, for example in devices with a maintenance function. The rings do not slip off the battery, which is why you can leave the charging process unattended with a clear conscience.
What types of car battery are there?
There are a total of three different types of car batteries. These differ in their composition and where they are used.
Lead-acid battery
This is the classic car battery that is installed in most vehicles. In some cases it is also called a lead-acid battery or accumulator. Lead plates are installed in the housing, which are in an electrolyte solution of diluted sulphuric acid. Lead-acid batteries are very cheap and last for several years. Most car battery chargers are compatible with these accumulators.
Lead-gel accumulator

Lead-gel accumulators are a further development of the classic lead-acid accumulators. Due to the addition of silicic acid, the electrolyte solution inside the battery is not liquid but gel-like. This is particularly advantageous when the battery is in a horizontal or inclined position. The loss of capacity is rather low with these models. Lead-gel accumulators, however, are only suitable for internal combustion engines to a limited extent and are mainly installed in electric cars; in some cases also in electric wheelchairs.
AGM accumulator

AGM stands for “Absorbent Glass Mat”. This is also a further development of the conventional lead-acid battery. The acid is bound in glass fibre mats. As a result, the batteries have improved properties: they are almost maintenance-free and there is hardly any danger of acid leaking out. AGM accumulators tend to be used in higher-priced cars and also boats, as they are comparatively expensive to manufacture. Not every conventional charger can charge such a battery.
The correct handling of car battery and charger
There is not much to consider with an automatic car battery charger, as the unit will do most of the work for you. Unless your unit is automatic, you will need to manually set what type of battery it is and what mode you want to use. You can then connect the charger to the house power. There is usually a display on the top that informs you of the charge level and mode.
When is the battery fully charged?
The charging time depends on the capacity and the charging current of the device. It is very easy to calculate: Divide the voltage of the device by the capacity of the battery. An average small car has a battery with a capacity of 60 ampere hours. A device with a charging current of 5 amperes takes about 12 hours to charge. Divide the voltage of the appliance by the capacity of the battery.
Three examples:
- 60 (ampere hours of the battery) / 5 (amperes of the charger) = 12 hours.
- 70 (ampere hours of the battery) / 7 (amperes of the charger) = 10 hours
- 80 (battery ampere hours) / 10 (charger amps) = 8 hours
What should be considered before connecting?
Make sure that all electrical energy consumers in the car are switched off before connecting the charger. This includes, for example, the lights, the radio and the navigation device if it is integrated into the car. Make sure that the battery is in a dry place protected from the weather, for example in a garage or under a carport. In this place, the air should be able to circulate sufficiently. Do not place the charger near an open fire or other heat source, such as a heater or oven.
Does the battery need to be disconnected before charging?
With most chargers, it is not necessary for you to disconnect the battery or even remove it from the engine. However, if you want to be sure or if it makes you feel better, there is nothing to stop you disconnecting the battery from the vehicle’s electronics. To do this, first remove the black or blue cable from the negative terminal and then the red cable from the positive terminal of the battery. You will need a spanner or screwdriver for this. Make sure that the battery’s vent holes are free before connecting the charger.
Connect the charger correctly
Clamp the charger’s connecting leads to the battery by first connecting the red clamp to the positive terminal and then the black or even blue lead to the negative terminal. When connecting, always grasp the plastic sheathing of the clamps and not the bare metal. When the clamps are tight, you can connect the unit to the mains.

Removing the charger correctly
When charging is finished, follow the steps in reverse order. First unplug the charger to cut off the power supply. Now remove the black or blue clamp from the negative terminal and then the red clamp from the positive terminal. If you have disconnected the battery from the vehicle electronics, you can now reconnect it: First connect the positive terminal and then the negative terminal. Tighten the connections with a spanner or screwdriver. They must never be loose or slip off.
Last but not least
If you proceed step by step as described above and pay attention to the correct execution, there are no risks for you. The charger’s functions provide additional safety. To ensure that your battery is not damaged, make sure to disconnect the charger unless it is a model with maintenance mode or automatic switch-off. Without appropriate protection mechanisms, your battery could overcharge or overheat.
With older, more high-maintenance batteries, it is also necessary to open the individual battery cells in order to discharge any gases that may be produced. Otherwise, there is a risk of fire or even explosion in the event of overcharging. This risk does not exist with conventional batteries, but only with batteries from vintage cars and other car models that are no longer manufactured today.
Charging without a charger
If your car won’t start and you don’t have a charger handy, there are two ways to get the car moving again
With a jumper cable
For this, you will need a second vehicle in addition to a jumper cable. Note that the battery voltage of the two vehicles must be identical. Place the cars close together and switch off the engines. Connect one end of the red jumper cable to the positive terminal of the flat battery and the other end to the positive terminal of the charged battery. First attach the black cable to the negative terminal of the second car’s battery and then to your car’s battery. It is especially important to make sure that the polarity is correct, as it can cause serious damage to both cars if you reverse the poles.
When both cables are correctly connected, first start the engine of the helping car. Then you can start the engine of your car. Let the engines of both vehicles run for three minutes. Switch on a large electrical consumer in your car, for example the lights or the ventilation, to avoid voltage peaks when disconnecting. Now you can remove the cables in reverse order. The engine must continue to run.
Starting the car
If you plan to start your car when the battery is flat, it should be a petrol car, as diesel cars cannot preheat without a working battery. You also cannot charge the battery of a car with automatic transmission by cranking it.
To start the car in this way, you need at least two people, as one person must sit in the driver’s seat. Switch on the ignition and shift into second gear. The driver steps on the clutch and lets it come slowly at about 10 kilometres per hour. Pushing the car becomes more difficult as soon as you let the clutch come. The car may jerk a little and lurch forward as soon as the engine starts.
















 3,410 reviews
3,410 reviews





