Fridge purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- What You Need to Know
- The refrigerator is one of the biggest consumers of electricity in the household. The energy efficiency class is therefore one of the most important criteria.
- The choice of types, sizes, designs and features is enormous. So there is exactly the right model for every household, but the choice is all the more difficult.
- A refrigerator that is too large consumes unnecessary energy. When buying a new appliance, it is important to choose one with a capacity that suits your lifestyle.
- Features such as automatic defrost, no-frost, cold storage compartments and the fast cooling system ensure energy-saving operation and optimum food storage.
- Modern refrigerators from the higher price segment can be integrated into the smart home network via WLAN and offer numerous convenience functions via app.
The refrigerator – A must in every household
The path to both healthy food and frustrating chocolate always leads us to one and the same place – the fridge in the kitchen.
The refrigerator is undoubtedly part of the standard equipment of a household. The Federal Statistical Office determined that in 2017, 99.9 percent of households in Germany had (at least) one refrigerator. A year earlier, the figure was exactly 100 percent. This makes the refrigerator the numerical front-runner among all major household appliances: The washing machine (2017: 96.4 percent) and the coffee machine (2017: 84.7 percent) are far behind.

Yesterday and today: the refrigerator in the household
A refrigerator in the household was not a matter of course for a long time. It was not until around 1950 that the household appliance began its triumphal march in Europe and also in Germany. Before that, people had to rely on cool pantries, especially in city flats, to store perishable food. In some old flats in Berlin, you can still find the so-called “Berlin refrigerator” – a built-in cupboard under the window where potatoes were stored.
Different refrigerator types
These indispensable household appliances are available in numerous designs, each with different features. This means there is something for every kitchen size and for small, medium and large households. There are also several options for integrating the appliance into the kitchen décor.
Typical refrigerator types
Freestanding refrigerators
Free-standing refrigerators are the most convenient to integrate. Owners can place a free-standing refrigerator anywhere in the kitchen or, if necessary, in another room in the flat. It requires no assembly and no special piece of furniture (keyword: conversion cabinet). These refrigerator classics are a recommendation if the kitchen furniture does not need a uniform front. Another practical feature is that owners can simply take their free-standing refrigerator with them when they move house. A classic freestanding appliance is also often used as a second appliance.

Freestanding refrigerators come in many designs: from classic white to modern stainless steel looks to eye-catching looks, such as the retro refrigerators by Bomann and Gorenje. The refrigerator can thus become a stylish eye-catcher in the kitchen.
A special form of the free-standing refrigerator is the so-called table refrigerator. With a height of 80 to 85 centimetres, it is about as high as a table. The small, compact freestanding appliance fits well in small households and also comes with a shelf. A well-known manufacturer of these small refrigerators is Exquisit.
Both refrigerator types are available as full-size refrigerators without freezer compartment or as compact refrigerators with freezer compartment.
Pro Points
- Flexible choice of location
- Variety of models and sizes
- Easy to take with you when you move
- Easy exchange of devices
- Can be used as storage/storage surface
Drawbacks
- No front to match the design of the kitchen furnishings
Built-in refrigerators
This type of refrigerator is built into the kitchen unit. A distinction is made here between two types: built-in refrigerators that can be integrated and those that can be decorated. The integrable models are installed in a conversion cabinet provided for this purpose. This piece of furniture is usually part of a built-in kitchen unit. However, there are also separate conversion cabinets for refrigerators on the market. In the case of refrigerators that can be decorated, a decorative panel can be attached to the front. Both installation options allow the refrigerator to be integrated seamlessly into the kitchen design, so that it fits unobtrusively into the style of the interior.
However, the built-in refrigerator must fit into the niche provided for it. When looking for a new integrated refrigerator model, consumers must therefore make sure that the dimensions are correct.
Consumers also have a wide choice of this type of refrigerator. There are built-in refrigerators with and without freezer compartments as well as fridge-freezer combinations.
Pro Points
- Space-saving
- Optics matching the kitchen design
- Variety of models and sizes
Drawbacks
- Installation by a specialist may be necessary
- Inflexible choice of location
Undercounter refrigerators
Undercounter refrigerators are quite similar to table refrigerators. However, many models have a removable top plate. This allows the user to attach a worktop to it that matches the kitchen unit. This makes the small refrigerator blend in even better with the interior. Since these refrigerators are not very high (about 80 to 85 centimetres), they can also be placed directly under an existing worktop without any complicated assembly. Unlike built-in appliances, they do not need a furniture cabinet for this. The small refrigerator stands on its own feet. The height of these can usually be adjusted so that the refrigerator stands level even on uneven floors.

As with the floor-standing and built-in appliances, the buyer of this type of refrigerator has a choice between full-size refrigerators and compact models with a small freezer compartment. Due to their small size, undercounter refrigerators are a recommendation for single households.
One disadvantage of the small refrigerators, however, is that they are not equipped with modern refrigerator functions such as no-frost, door alarms or freshness compartments.
Pro Points
- Space-saving
- Less expensive than small built-in units
- Wider choice of different models
- Can be used as a second unit or minibar
Drawbacks
- Few functions and features
- Available storage space quite limited
Special refrigerator types
In addition to these standards, there are several special forms and modern refrigerator types on the market, which we briefly introduce here.
Fridge-freezers
This combination of fridge and freezer is practical when there is no space for two appliances in the kitchen. The two components are arranged one above the other and fit into many refrigerator niches in a kitchen. The advantage compared to the refrigerator with freezer compartment is the larger freezer section. It has its own door and usually contains two to three drawers for the frozen food. This makes these appliances a recommendation for consumers who like to freeze pre-cooked food or pastries, for example. The refrigerator compartment also offers enough space for a small family’s weekly shopping.

One disadvantage of the combination unit, however, is that a partial unit cannot be replaced in the event of a defect.
The practical fridge-freezers are available as freestanding appliances in various designs and sizes as well as built-in appliances. The fridge-freezers from Beko are very popular.
Pro Points
- More space-saving than two individual units
- Larger freezer area than the refrigerator with freezer compartment
- Lower acquisition costs compared to two individual units
Drawbacks
- Defective sub-unit cannot be replaced individually
Side-by-side refrigerators
Many consumers in this country know the double-door giant refrigerators from American TV series. That is why they are also known as “American refrigerators”. They are a refrigerator-freezer combination of a special kind. The two sub-units are not, as usual, arranged one above the other, but side by side. Each has its own door, so that the refrigerator resembles a large wardrobe.
Consumers have a choice between American and European models of this type of refrigerator. American refrigerators are a single appliance, with the freezer section often slightly narrower than the refrigerator section. European side-by-side refrigerators, such as those made by Bauknecht or Liebherr, are two appliances coupled together by a connector.

Side-by-side refrigerators offer a lot of space, but also take up a lot of room in the kitchen themselves. This makes them a recommendation for large households with four or more people. The energy consumption of side-by-side refrigerators is also higher than that of conventional refrigerators. The separate cooling circuits, which allow separate temperature control, are advantageous. In addition, side-by-side refrigerators are usually equipped with innovative functions, such as water and ice cube dispensers, bar compartments and door-in-door or Wi-Fi functions. The variety of comfort features is ultimately also reflected in the price tag.
Pro Points
- Plenty of storage space in the refrigerator and freezer area
- Innovative extra functions
- Dynamic cooling
- Separate cooling circuits
- Different temperature zones for optimum food storage
Drawbacks
- Need a lot of space
- High energy consumption
- Relatively expensive
French-door refrigerators
A variant of the double-door refrigerator is the French door refrigerator. In this type of refrigerator, the cooling section has a hinged door. The freezer section is usually located below the refrigerator section and is distributed over several drawers.
The advantage of a French door refrigerator is the large amount of space in the cooling area. This is also conveniently located at eye level. Compared to the classic side-by-side refrigerator, “the French door” requires less space. Nevertheless, it is better off in a large kitchen and in a multi-person household than in a cramped room. This refrigerator also offers extra functions such as a water dispenser or separate cooling circuits. Bauknecht, Bomann or Samsung are well-known manufacturers of this type of refrigerator.

Pro Points
- Large capacity
- Relatively narrow for a double-door refrigerator
- Dynamic cooling
- Separate cooling circuits
- Extra functions
- Different temperature zones for optimum food storage
Drawbacks
- Higher energy consumption than a conventional refrigerator
- Relatively expensive
In addition, there are other different special forms such as drinks refrigerators, wine refrigerators or mini refrigerators.
Here’s what you should look for when buying a refrigerator
When answering the question of which refrigerator is best suited for which consumer, there are several aspects to consider. A refrigerator is usually a purchase for as many years as possible. Of course, it should therefore be the best of all, have an attractive design and a reasonable price. However, the model that comes first in a test is not automatically the refrigerator that is recommended for every household.
Various criteria play a role in choosing the right refrigerator. To give consumers a better orientation, we present the most important factors for the purchase decision.
Size and useful capacity
First of all, the room layout in the kitchen plays a major role. This is where it is decided which type of refrigerator (free-standing, built-in, under-counter or double-door) comes into question.
In addition, the useful capacity is important. This value indicates how much space the refrigerator offers for storage. For models with a freezer compartment or freezer section, the usable volume for the refrigerator and freezer sections is indicated separately.
A refrigerator with a high useful capacity consumes more energy. According to the consumer advice centre, 100 litres more usable capacity increases the electricity consumption of the refrigerator by about 20 percent. Therefore, it is advisable, especially when buying a new appliance, to buy a refrigerator in the size that corresponds as closely as possible to your personal needs.
Determine the need
A common guideline for households of one to two people is about 100 to 140 litres of refrigerator space. For each additional person, add about 50 litres.
When determining the requirements for the freezer, it also depends on the storage. If you regularly freeze large quantities of fruit and vegetables, for example from your own garden, you will need more space than someone who only stores a few frozen provisions from the supermarket. The usual recommendation for a two-person household with a small stockpile is about 50 to 80 litres. For larger stockpiles, 100 to 130 litres are appropriate for the freezer section.
The following overview shows the guideline values that experts recommend:
| Household size | Recommended usable capacity (refrigerator) | Recommended usable capacity (freezer compartment) |
| 1 person | 80 to 100 litres | 30 to 50 litres |
| 2 persons | 120 to 150 litres | 50 to 80 litres |
| 3 persons | 160 to 200 litres | 60 to 100 litres |
| 4 persons | 200 to 250 litres | 75 to 125 litres |
| 5 persons | 240 to 300 litres | 90 to 150 litres |
Energy consumption
Electricity consumption is always essential when buying a new household appliance, because this value determines the follow-up costs of the appliance for the buyer during the years of its use. It is also a good way to compare several shortlisted refrigerators. It can pay off to invest in a refrigerator with energy efficiency class A+++. These are admittedly somewhat more expensive to buy. In the long run, however, consumers save this money again in electricity costs.
Because the energy efficiency class is a decisive factor when buying large household appliances, we devote a separate chapter to this topic. There, interested parties will find more detailed information on the electricity consumption of refrigerators, a sample calculation of cost savings as well as energy-saving tips.
Volume
The volume of the refrigerator as a selection criterion should not be underestimated. After all, the appliance finds its place in the kitchen, i.e. in the room where families and flatmates often gather. A loudly humming refrigerator can quickly become a nuisance. Even in an open kitchen, it can be annoying if the refrigerator’s compressor does its work too loudly.
The noise level of a household appliance is expressed in decibels (dB). The normal value of refrigerators is about 45 to 50 decibels. This corresponds approximately to the volume of a normal conversation. Refrigerators with a noise emission of 39 decibels or less are quiet appliances. A value of around 35 decibels is particularly recommended. This volume is comparable to the whirring of a room fan and is therefore as quiet as a whisper.
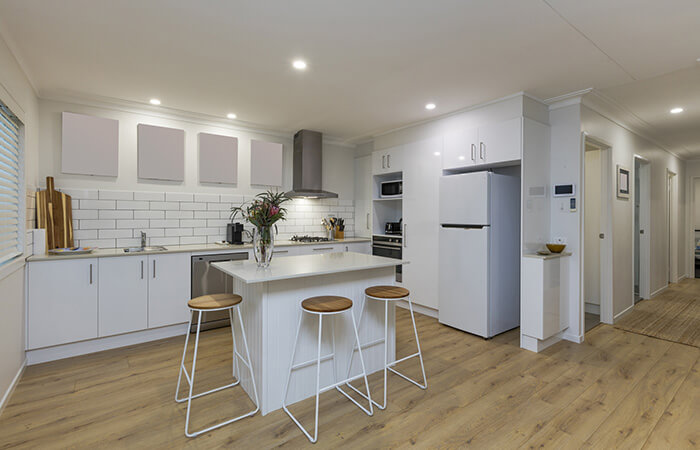

Material
It is also worth looking at the material used in the refrigerator. Modern refrigerators are often equipped with high-quality stainless steel doors. The shelves should be made of safety glass. This is shatterproof and scratch-resistant. If you want a model with bottle storage, make sure that the grille is made of metal.
After these technical factors, consumers should also be aware of the most important aspects regarding the equipment, range of functions and extra features of refrigerators in order to make the optimal purchase decision for themselves.
Zero degree zone

New refrigerators usually have several temperature zones and compartments with different humidity levels. This ensures more appropriate storage of the different foods, preserving vitamins and flavours. Almost all manufacturers integrate so-called cold storage compartments. In these, the temperature is just above freezing point. This degree of cold is optimal for storing fresh food such as fruit, vegetables, meat, fish and some dairy products. However, each manufacturer has its own name for this new refrigeration technology. Bosch, for example, speaks of the VitaFresh zone, while Miele touts a PerfectFresh compartment. Some manufacturers divide this zero-degree zone into a dry and a humid area. Each drawer has a different humidity level. Meat and fish, for example, do well at around zero degrees Celsius and a humidity of about 50 per cent. Vegetables and fruit, on the other hand, need more water. They stay crisp and fresh in zero-degree fresh compartments with a humidity of about 95 per cent. The advantage of this equipment: the food keeps longer. The consumer has to throw away less food due to over storage and spoilage and gets more out of his purchase.
Automatic defrost

The more the refrigerator ices up, the lower its cooling capacity becomes. At the same time, energy consumption increases. In the past, users therefore had to defrost the refrigerator regularly. Today, refrigerators have an automatic defrosting system. Before a layer of ice forms on the inside walls of the appliance, the refrigerator increases the temperature for a short time. This defrosts the layer of frost. The water runs along the wall into a drain channel and is directed outside into an evaporation tray. This eliminates the need to constantly defrost the refrigerator. This feature can now be found in all new refrigerators, in every price segment. Automatic defrosting in the freezer compartment, on the other hand, is not a standard feature.
No-frost function
The no-frost function and the less powerful low-frost function also ensure that hardly any ice forms inside the refrigerator. This works through a ventilation system that reduces the humidity in the refrigerator compartment. This results in less frost and ice forming. The formation of ice cannot be completely avoided because warm air and moisture always enter the refrigerator when the door is opened and closed. If a layer of frost forms in the appliance, the automatic defrost intervenes. A combination of both functions is therefore the best recommendation. It offers the most convenience for the user and contributes to economical energy consumption.
Fast cooling function
The following applies to many foods: the faster they are brought to the cooling temperature in the refrigerator, the better their quality is preserved. This is especially true for foods that consist largely of water, such as fruit and vegetables. The blast chilling function lowers the temperature considerably for a short time. The freshly stored food is thus quickly brought to the storage temperature. Afterwards, the refrigerator switches off the express cooling again and returns to normal operation. Analogous to express cooling, some refrigerators with freezer compartments or some fridge-freezers are equipped with a quick-freeze function.
Extras and luxury features for the refrigerator
In addition to the important cooling and freezing functions, refrigerators are equipped with other extras that make them convenient to use. Modern refrigerators offer the following additional functions:
Antibacterial coating

Some models have an antibacterial layer on the inside walls of the refrigerator. This promises even more hygienic food storage. Even more hygienic because the cold already inhibits the growth of bacteria and mould. An antimicrobial coating with silver compounds is supposed to additionally reduce the germ load in the refrigerator. However, experts, for example from the Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR), are critical of this measure. There is no evidence that such a coating offers additional advantages. In any case, consumers should continue to clean the refrigerator regularly.
Anti-Fingerprint

As beautiful as the stainless steel fronts look, they are very susceptible to fingerprints. To ensure that the refrigerator retains its high-quality appearance for a long time, manufacturers use a special coating that largely prevents the unsightly finger marks. Another advantage for the consumer: the household appliance does not require such frequent external cleaning.
Indoor fan
Usually, the air in the refrigerator is distributed unevenly. It is colder at the bottom than in the upper compartments. This static cooling results in different temperature zones and recommendations as to which food should be stored in which compartment. In refrigerators with dynamic cooling, an interior fan distributes the air evenly. Differences in temperature and humidity are thus cancelled out.
Water and ice cube dispenser

Especially the large side-by-side refrigerators and the French-door refrigerators are equipped with this luxury feature. At the touch of a button, the user draws fresh drinking water or fills his glass with ice cubes. This function requires either a fixed water connection or a built-in water tank that takes up some extra space. In addition, the water tank requires more cleaning.
Display

In addition to the cooling capacity and storage conditions, manufacturers are also constantly improving the operation of the refrigerator. New refrigerators in the higher price range often have a display for control. The user can regulate the temperature to the exact degree, operate the water dispenser and select the quick-freeze functions. If the refrigerator is equipped with a door alarm, the display gives the user a visual warning of the temperature rise. Samsung has built a large LC display into some models, which works like a tablet and allows access to recipe apps and calendars.
Smart home connection

Since the refrigerator is one of the most common household appliances, it is not surprising that it is increasingly being integrated into smart home networks. Although this is currently only possible with models from the higher price segment, it is no longer a pipe dream. Smart refrigerators have Wi-Fi functions. The user controls the temperature or carries out a fault diagnosis via an app. Samsung has even built food cameras into some appliances. This allows the user to take a look at the supplies in the fridge remotely via an app. This is practical when you are in the supermarket and no longer know whether the eggs in stock are still enough for a planned recipe. Smart refrigerators can also record the expiry date of the stored food, suggest recipes to match the available stocks, display the nutritional values of the food, suggest in which compartment it should be optimally stored, create shopping lists and order the food online from a delivery service at the user’s request thanks to a Wi-Fi connection.
These new functions are not just gimmicks. Rather, they provide energy savings, for example, because the user does not have to open the door as often to inspect the contents of the refrigerator. They also help to produce less organic waste because the user does not buy too much or twice and uses up the refrigerated supplies in time.
The energy consumption of the refrigerator
A refrigerator is in constant use – 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. For this reason, energy efficiency is an important factor to consider when making a purchase. After all, electricity consumption results in follow-up costs that are not visible on the product’s price tag. It is therefore worth taking a look at the EU energy label.
The EU energy label
This label classifies electrical appliances into different energy efficiency classes. The scale ranges from A to G and is represented by coloured bars. Similar to the American school grading system, A (green) is the best grade and G (red) the worst. Because manufacturers have brought better and better appliances onto the market, a distinction is now also made between the classes A, A+, A++ and A+++.
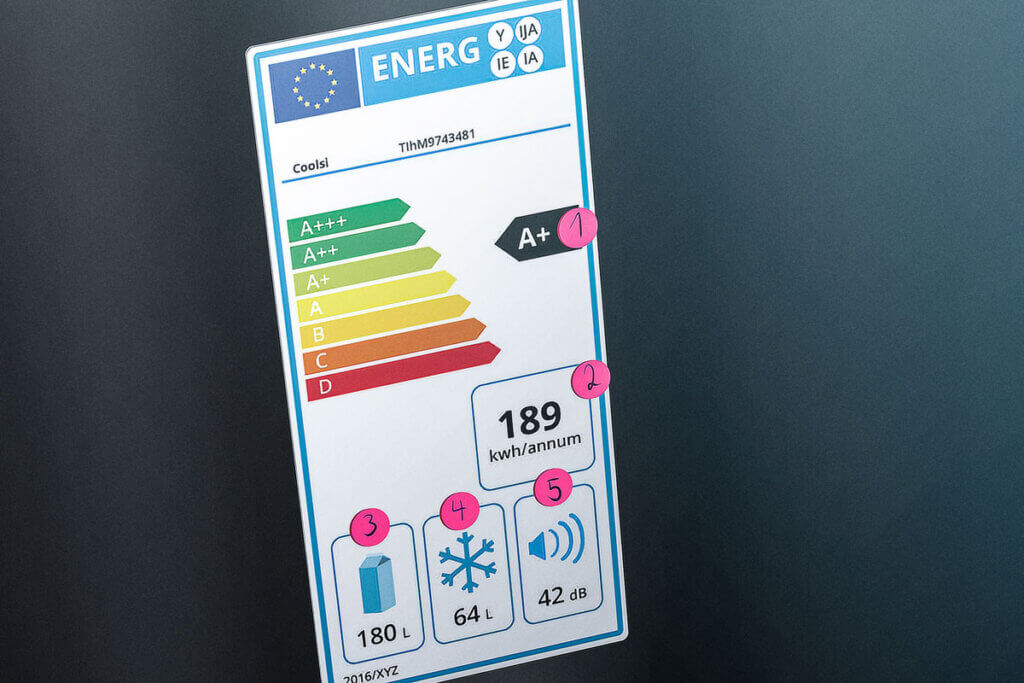
Since 2012, only refrigerators and freezers that meet at least the A+ standard may be sold in stores in the EU. The classes E to G therefore disappeared from some labels.
The A classes of energy efficiency
A+++ is the most economical energy class. The appliances that meet this standard are usually more expensive than appliances in the lower A classes. What is the difference between the various A-level energy classes? Is the surcharge worth it?
In general, the following guide values can be assumed: A class A++ appliance consumes about 25 per cent less energy than an A+ appliance. The difference between A+++ and A+ is even 50 percent.
The following table illustrates this in concrete figures. We are comparing a fridge-freezer combination with a total useful capacity of about 300 litres (of which about 85 litres for the freezer section):
| Energy efficiency class | A+ | A++ | A+++ |
| Annual electricity consumption | 326 kWh | 235 kWh | 161 kWh |
| Average electricity costs for 10 years in euros (at 0.29 euros/kWh) | 939,50 € | 686,00 € | 464,50 € |
| Savings compared to A+ in 10 years | – | 253,50 € | 475,00 € |
So it pays off in the long run to choose a refrigerator with a high energy efficiency rating.
Future prospects
The EU Parliament decided in 2017 to return to the original energy class division from A to G. This means that the division of class A into several plus classes (A+, A++ and A+++) will be abolished again. A new version of the EU energy label is expected to be on sale from 2020.
Save energy with the refrigerator
The information on annual electricity consumption on the EU label or in the product description should be understood as average values. How much energy the refrigerator actually consumes also depends on its everyday use. If you follow a few tips here, you can save a few more euros on your electricity bill.
- The refrigerator works more energy-efficiently when it is well filled. Empty rooms quickly fill with (warm) air when the door is opened. The subsequent cooling of the air consumes an unnecessary amount of energy.
- Consumers should choose a model whose space fits their storage needs. A refrigerator that is too large for the household quickly becomes an energy guzzler.
- The inside temperature should be reasonably cool. It is sufficient if there are about 5 to 7 degrees Celsius in the refrigerator. For the freezer compartment, experts recommend about -18 degrees Celsius. Cooling to very low temperatures is reflected in energy consumption.
- The refrigerator door should be opened as rarely as possible and preferably only briefly so that only a little cold air escapes.
- Do not put warm food in the refrigerator! It takes a lot of energy to compensate for this temperature difference. It is better to cool food completely to room temperature before putting it in the refrigerator.
- The installation location is also a decisive factor for the energy-saving use of the refrigerator. For example, the appliance should not be placed near sources of heat such as the cooker or heater, or by a window with long hours of sunlight during the day. However, modern refrigerators with good insulation are much less sensitive to the outside temperature than appliances that were on the market about ten or more years ago. Consumers can therefore be a little more relaxed about this criterion.
Putting the fridge away properly – making the best use of temperature zones
When saving energy, it also helps to use the different temperature zones and the cold storage and fresh food compartments of the refrigerator effectively. In refrigerators with an interior fan, the temperature is balanced. So it doesn’t matter in which compartment the milk is and in which the sausage is.
In refrigerators without a fan, the air circulation causes the warm air to rise upwards while the cold air sinks downwards. This creates different temperature zones that the consumer should use for optimal food storage.
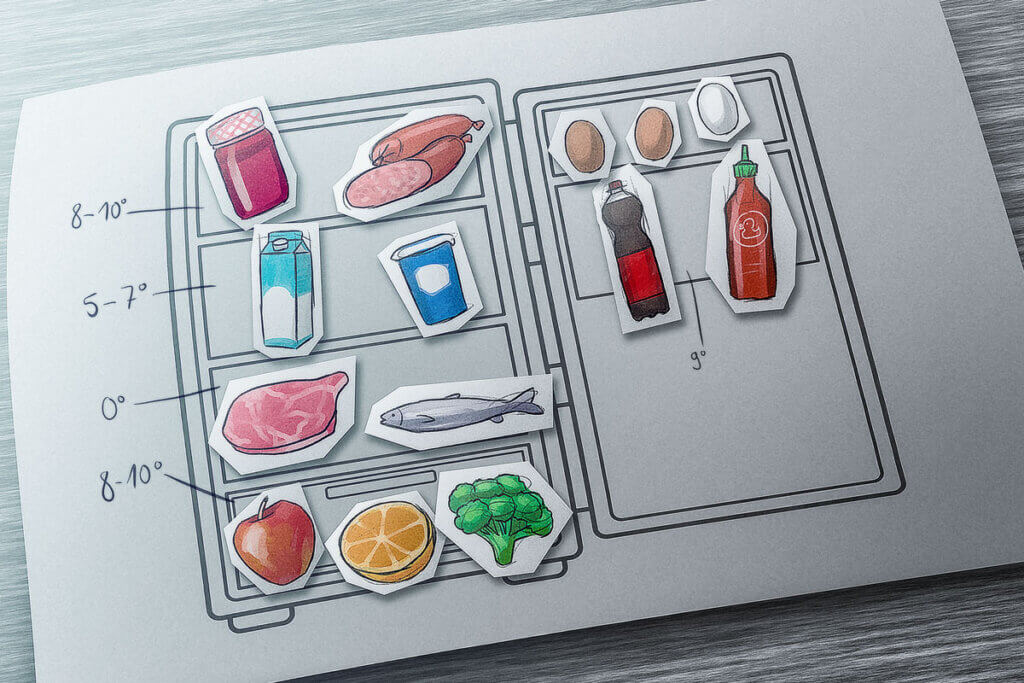
- Upper compartment – warm zone: The temperature is between 8 and 10 degrees Celsius. Jam, packaged cheese or cooked food are all good here.
- Middle compartment – Middle zone: Dairy products stay fresh for a long time at a temperature of about 5 degrees Celsius.
- Lower compartment – cold zone: At about 2 degrees Celsius, this is the coldest temperature in the refrigerator. This condition is optimal for storing raw meat, fish and other quickly perishable foods.
- Vegetable drawer – Special zone: The plastic drawer is covered by a glass plate at the top. This ensures that the cold air does not sink any further. The temperature in the vegetable compartment is again around 8 degrees Celsius. Vegetables and fruit stay crisp and fresh here for longer.
- Door compartments: The temperature is relatively warm at around 9 degrees Celsius. The narrow compartments are suitable for drinks and sauces. The top compartment is mostly for eggs and butter.
How does a refrigerator work?
The refrigerator ensures that the food stored in it stays fresh for longer. This works because the cold temperature that prevails inside the appliance makes the biological and chemical processes run more slowly.
This cooling is carried out according to the same principle in all types of refrigerators: the appliances extract heat from the interior, conduct it outside and release it into the environment. However, there are several methods for carrying out this principle. One of them is the compression method. This is also used in most household refrigerators.
The compression principle in the refrigerator
A compression system consists of an evaporator, compressor, condenser and throttle. The heat transfer takes place with so-called refrigerants. These are liquids that evaporate into gas under the influence of heat.
The evaporator is a system of tubes which – depending on the model – is located in the side walls, the floor and the rear wall of the refrigerator interior. The liquid refrigerant inside flows into the refrigerator. When it comes into contact with heat from the interior, it evaporates into gas. In this form, it reaches the compressor, which is located on the outside at the lower rear of the refrigerator.
The compressor compresses the gas so that it heats up. It is then passed through the condenser. This is the coiled, black tube system located at the back of the refrigerator. As the refrigerant makes its way through the tubes, it releases heat into the environment. As it cools, it condenses, which means it turns back into a liquid. This is how it flows through the choke. This device lowers the pressure of the refrigerant once more. Then the refrigerant flows back into the evaporator and the cycle starts again.
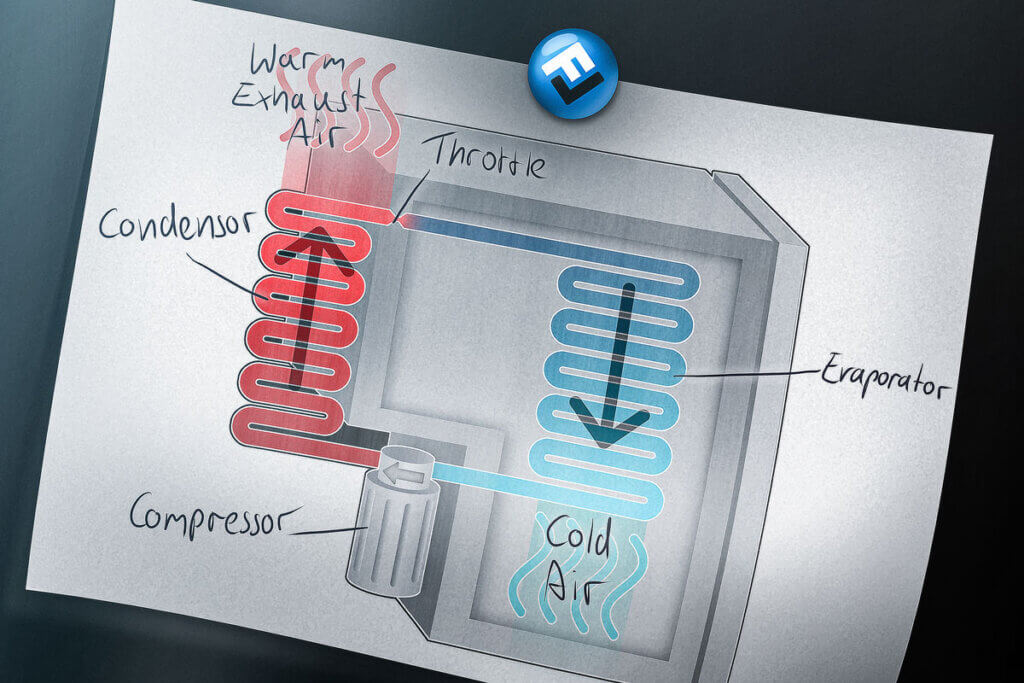
The disadvantage of the compression system is the noise generated by the compressor. This is driven by a motor.
The silent alternative
Another method of heat transfer used in refrigerators is absorption. However, this should only be mentioned here for the sake of completeness, as it does not occur in conventional household refrigerators. In contrast to the compression method, this cooling system runs silently. However, it consumes a lot of energy. Therefore, it is primarily used for mini refrigerators, cool boxes and minibars.























 699 reviews
699 reviews



